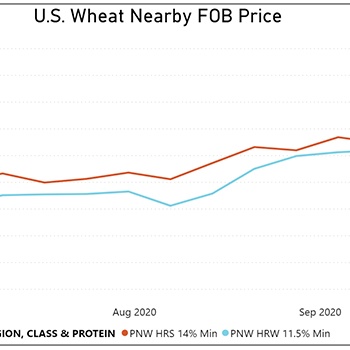
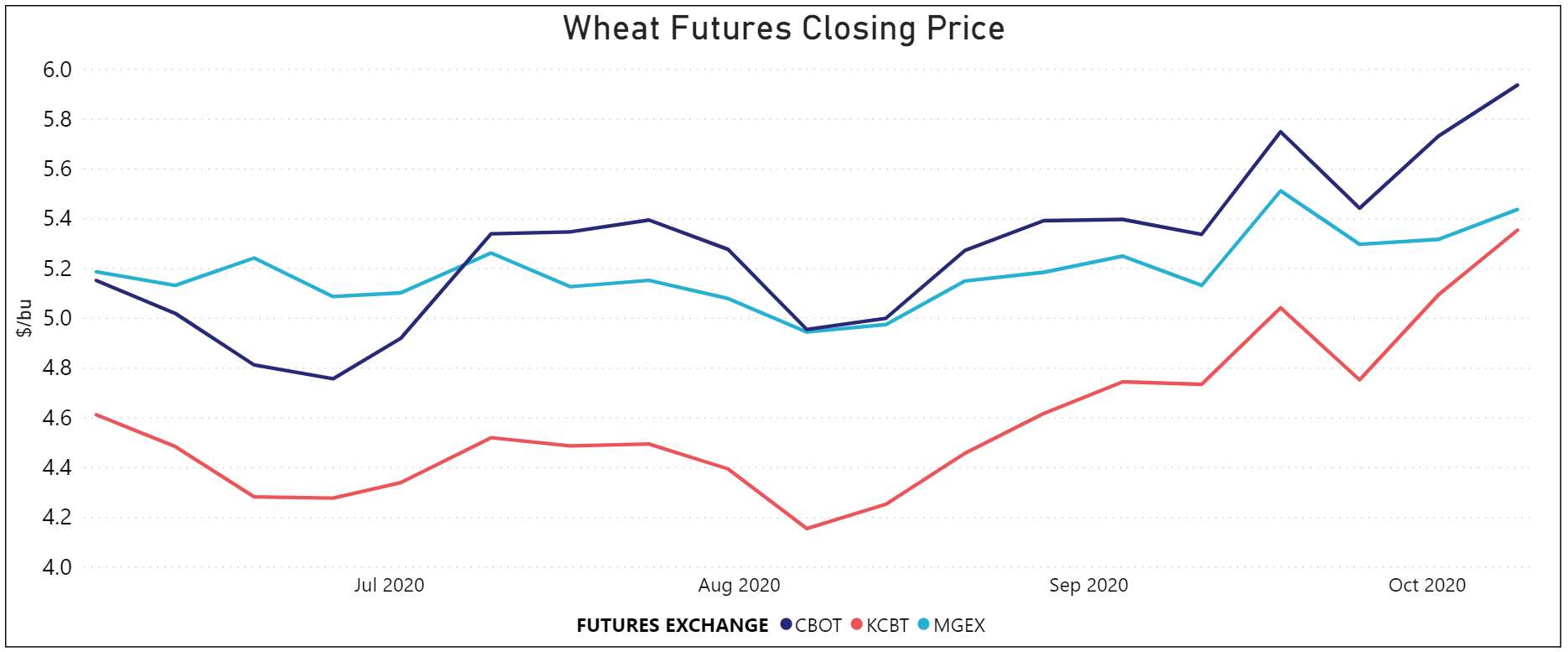
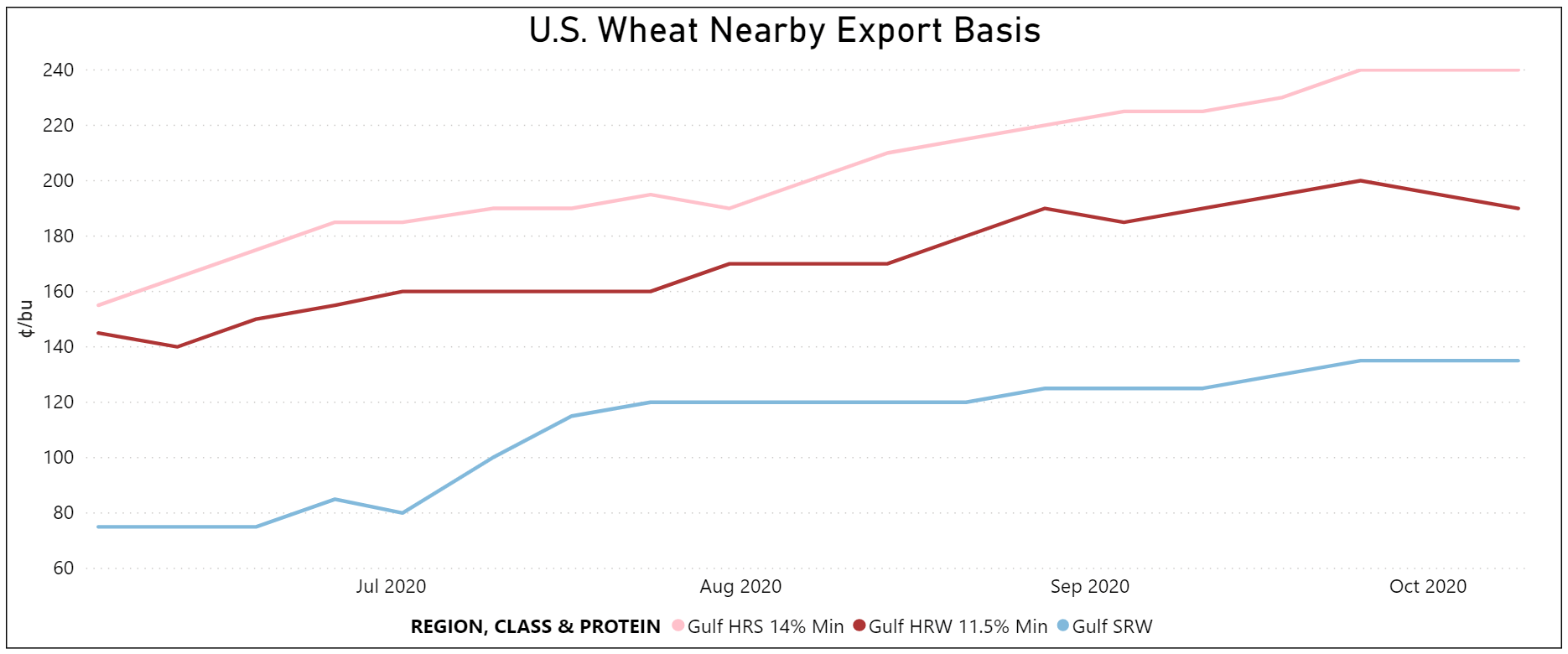
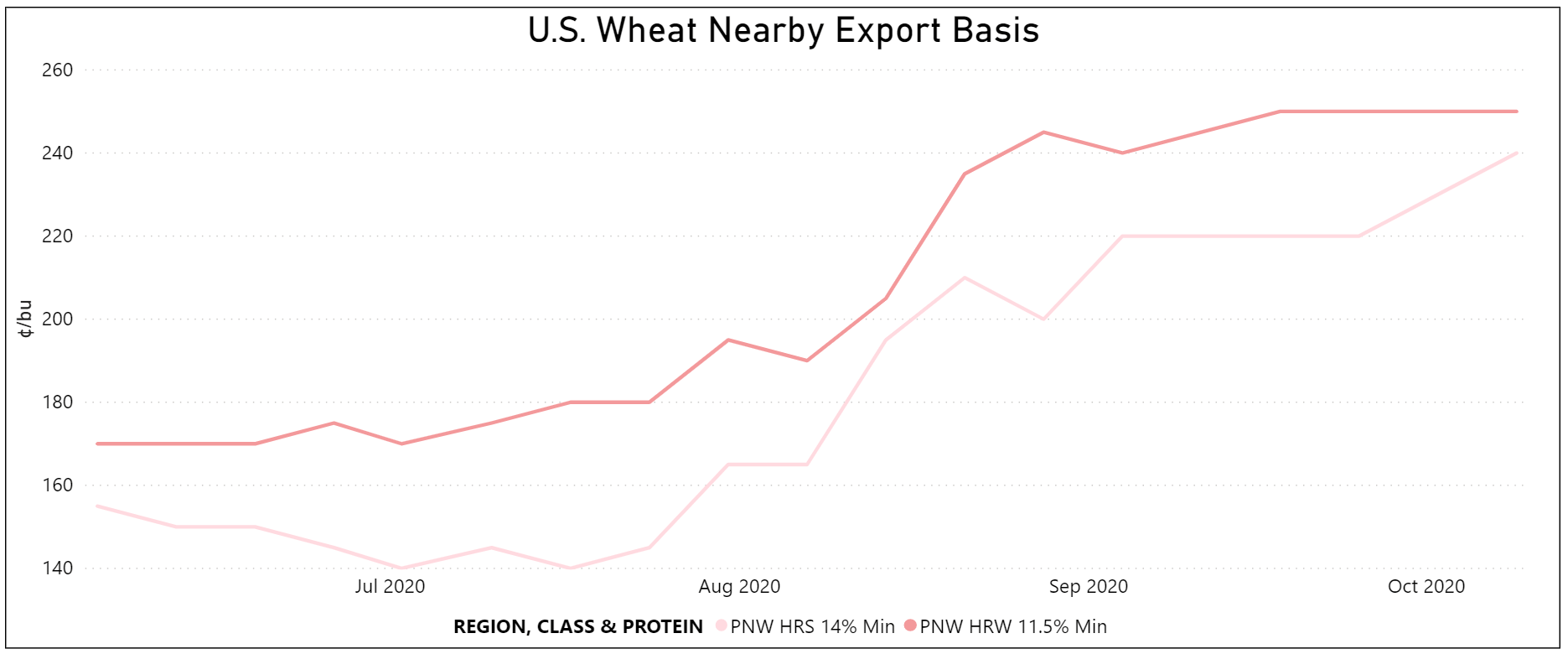
By Claire Hutchins, USW Market Analyst
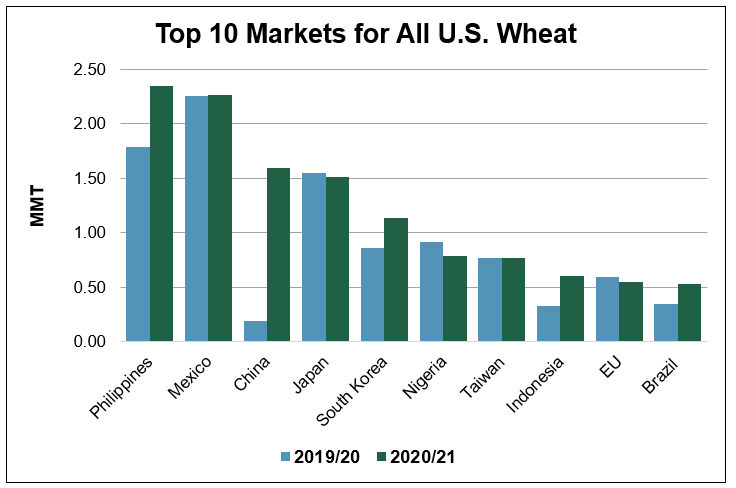
USDA estimates the United States will export 25.9 million metric tons (MMT) of wheat in 2020/21, 2 percent behind last year’s pace if realized. However, two months into marketing year (MY) 2020/21, total U.S. wheat commercial sales are 8 percent ahead of last year’s pace at 9.62 MMT and are 12 percent ahead of the 5-year average.
To date, export sales of hard red spring (HRS) wheat, white wheat and durum are significantly ahead of last year’s pace. Sales of hard red winter (HRW) wheat are nearly in line with last year, while sales of soft red winter (SRW) lag 2019/20. Success in individual markets such as China and Brazil due to policy changes and strong education programs by U.S. Wheat Associates (USW) are supporting overall sales. As in other markets, competitive pricing for U.S. wheat is helping fuel a faster import pace by traditionally strong U.S. wheat buyers like the Philippines, Japan and South Korea.
Here is more detail about the current factors underlying U.S. wheat export sales.
HRS. Total HRS export sales of 2.85 MMT are 28 percent ahead of this time last year and are 12 percent ahead of the 5-year average. Sales to the Philippines, the top market for HRS, are 23 percent ahead of last year at 768,000 MT and are 52 percent ahead of the 5-year average. Rising per capita consumption combined with population growth and competitive HRS prices are supporting strong sales to the Philippines early in MY 2020/21.
In Japan, the second largest market for HRS, sales of 379,000 MT are up 52 percent on the year.
“We had good start this year in the Japanese market following the U.S. and Japan trade agreement implemented on January 1,” said Rick Nakano, USW Country Director in Japan. “This gives U.S. wheat a better opportunity to be traded on equal footing with similar classes of wheat from Canada. This results in a great outcome for U.S. wheat to satisfy the needs of Japanese millers that now pay the same price mark-up as for Canadian wheat. Additionally, the relative price increase for Canadian spring wheat has also supported HRS demand in the Japanese market.”
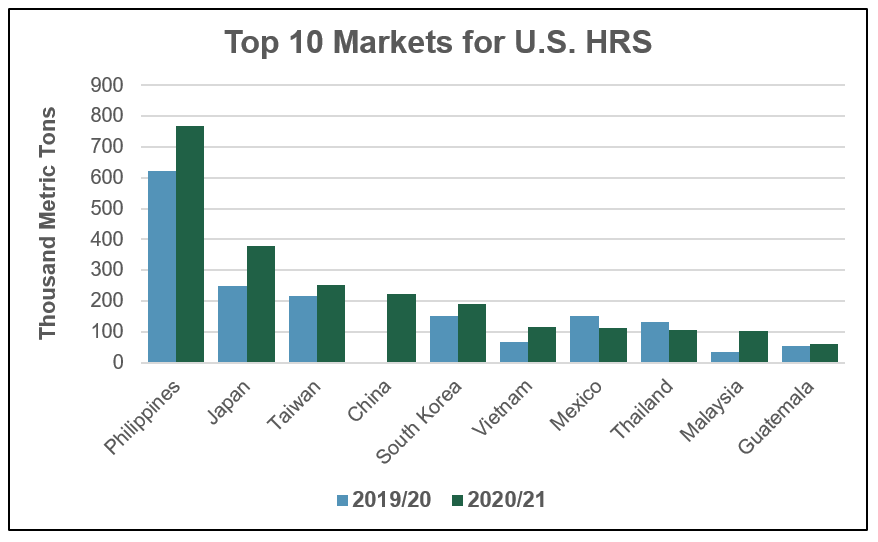
Source: USDA ERS export sales data as of July 23, 2020
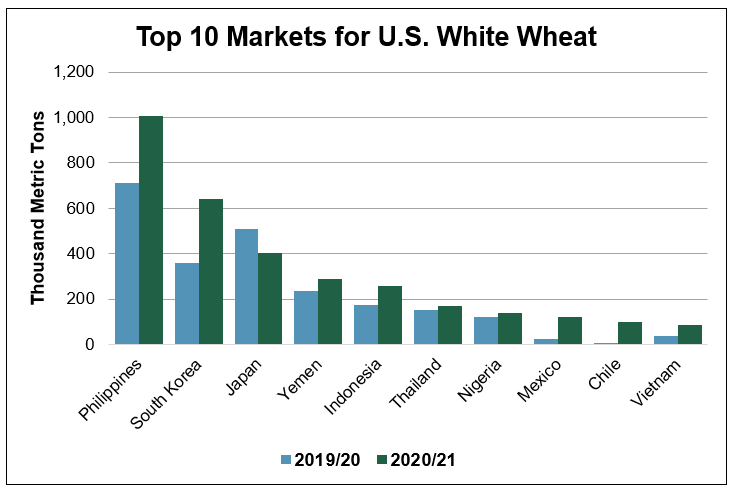
White. Total U.S. white wheat sales are 23 percent ahead of last year at 1.93 MMT, 12 percent ahead of the 5-year average. In South Korea, the second largest market for U.S. soft white wheat, export sales are up 27 percent on the year and are 4 percent ahead of the 5-year average.
“The price of U.S. white wheat has been much more competitive than comparable Australian classes during the first and second quarter of 2020,” said C.Y. Kang, USW Country Director in South Korea. Kang added that HRS and U.S. white wheat sales to South Korea are up on the year in part because South Korean instant noodle production is up on increased demand during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Sales to Japan, the third largest market for U.S. white wheat are 3 percent ahead of this time last year at 235,000 MT.
“The demand for U.S. Western White (WW) wheat, a blend of U.S. soft white wheat and U.S. club wheat, has been stable in Japan with strong consumption for confectionery products including sponge cake and biscuits. U.S. WW is a unique product and cannot be substituted by Australian, Canadian or domestically grown Japanese wheat,” said Nakano.
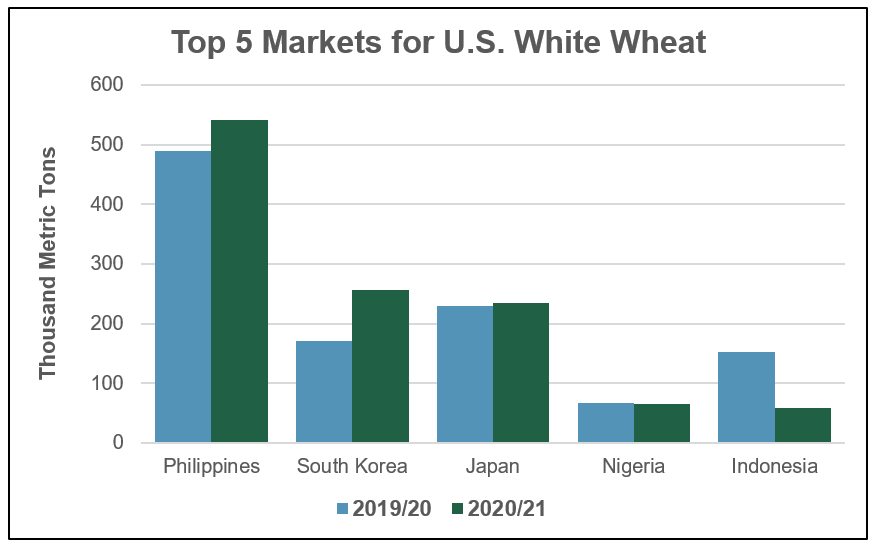
Source: USDA ERS export sales data as of July 23, 2020; about 99% of white wheat sales are soft white and soft white sub-classes
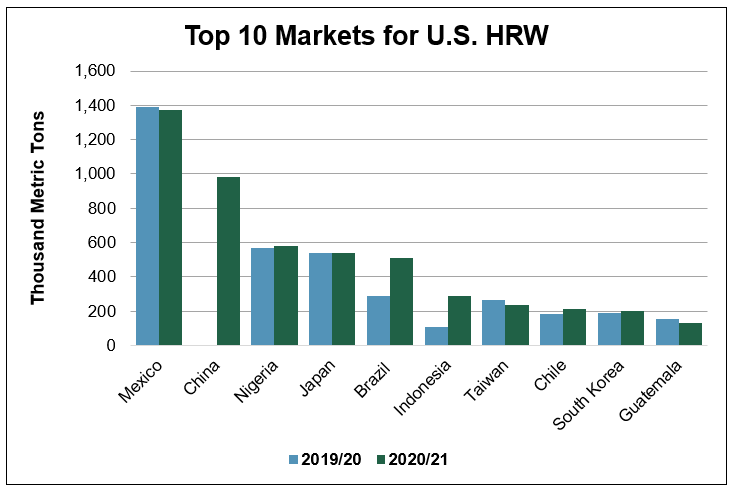
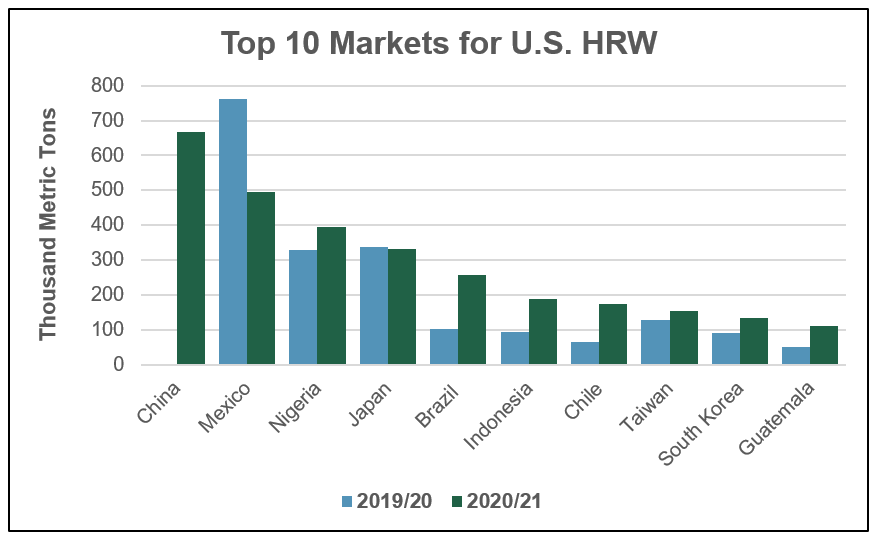
HRW. Total HRW sales are slightly below last year at 3.52 MMT, but 21 percent ahead of the 5-year average. Strong export programs to China and Brazil are supporting HRW sales in the first few months of 2020/21.
As of July 23, China has purchased 669,000 metric tons (MT) of HRW after no purchases in 2019/20. Strong HRW export sales so far in 2020/21 can be attributed to the Phase One agreement between the United States and China and HRW’s competitive prices compared to other classes of U.S. wheat. So far in marketing year 2020/21, China is the largest market for HRW.
HRW export sales to Brazil are more than double this time last year at 257,000 MT and are 85 percent ahead of the 5-year average. According to Miguel Galdos, USW Regional Director in South America, increased sales to Brazil can be attributed to the Brazilian government opening a tariff rate quota (TRQ) which allows up to 750,000 MT of non-Mercosur (South America’s free trade bloc) wheat to enter the country tariff-free. Strong educational programs in Brazil by USW are encouraging millers to take advantage of the high quality and competitive prices of U.S. wheat. To date, Brazil is the fifth largest market for HRW.
“USW provides the best trade and technical service to our customers and we are here for Brazilian mills for any need they have,” said Galdos.
Source: USDA ERS export sales data as of July 23, 2020
Durum. Total durum export sales are 6 percent ahead of this time last year at 385,000 MT and are 57 percent ahead of the 5-year average. Export sales to Italy, the largest market for U.S. durum, are more than double this time last year and are significantly higher than the 5-year average.
“Italy needs the high protein content of durum from North America, because it does not produce enough high protein durum locally,” said Rutger Koekoek, USW Regional Marketing Director for the European Region.
It is expected that Italy will produce an average volume of durum this year and will need to import large volumes of North American durum wheat again in MY 2020/21.
“I am still expecting an above average export volume of U.S. durum to Italy this marketing year,” said Koekoek.
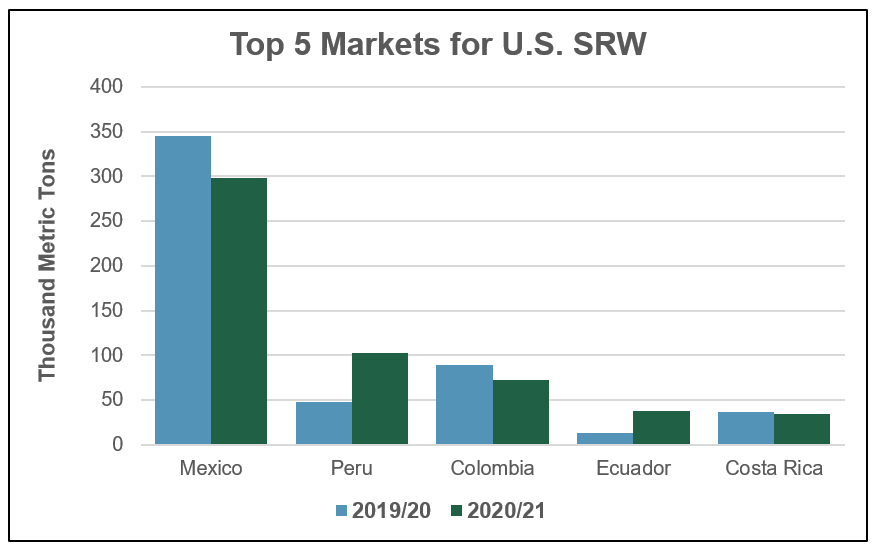
SRW export sales are a different story. Total SRW export sales are down 21 percent on the year to 927,000 MT, 17 percent behind the 5-year average.
“It is a price story,” said one grain trader, “we’re priced out of the world market, especially to our buyers in Latin America and Nigeria.” Between early January and late July, the average export price for SRW was $234/MT, 8 percent higher than the same period last year and 12 percent higher than the 5-year average.
In Colombia, the second largest market for SRW, export sale of 73,000 MT are 18 percent behind last year’s pace and 22 percent behind the 5-year average.
“Colombian mills bought more wheat than they needed between March and May due to demand uncertainty around COVID-19. They are now covered for the next couple of months. Higher prices are also impacting 2020/21 SRW sales to Colombia,” said Galdos.
High SRW export prices early in 2020, which continued into late July, are also having a significant impact on SRW demand in Nigeria, which has imported no SRW yet in 2020/21.
Source: USDA ERS export sales data as of July 23, 2020