U.S. Wheat Associates (USW) and the National Association of Wheat Growers (NAWG) unveiled the results of an econometric study showing that excessive farm support in several advanced developing countries could cost U.S. wheat farmers nearly $1 billion in revenue every year. USW recently showed that the governments of China, India, Turkey and Brazil have dramatically increased subsidies for domestic wheat production over the past ten years to levels that far exceed their World Trade Organization (WTO) agreements. This study confirms that these policies have a detrimental effect on U.S. and world wheat farmers and global wheat trade.
“I believe we have shown through these studies that the old perceptions about farm support and trade are clearly wrong,” said USW President Alan Tracy. “Today, it is the farm subsidies in a few advanced developing countries, not developed country policies, which disrupt normal trade flows and distort world wheat prices. These rapidly growing subsidies cause direct, serious and now measurable impacts on the prices that U.S. farmers receive for their grain.”
Noted agricultural economist Dr. Dermot Hayes and two of his colleagues at Iowa State University conducted the study. The goal was to determine what would happen to U.S. and global wheat production, trade and prices if domestic support in China, India, Turkey and Brazil were removed. To accomplish this, Dr. Hayes and his colleagues applied the price support and input subsidy data identified in a November 2014 study by DTB Associates to the respected CARD-FAPRI econometric model. Results showed that if all support were removed from all four countries, annual U.S. wheat production would increase by more than 53 million bushels, farm gate prices would increase by nearly $0.30 per bushel and U.S. wheat farmers would receive $947 million more in annual revenue (See Chart 1).
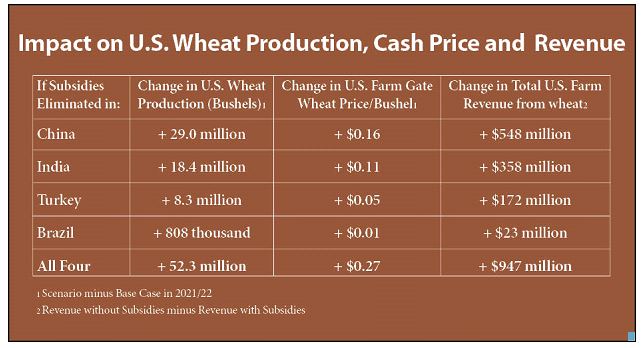
“The results confirm that if domestic support were removed wheat prices in the countries modeled would go down and farmers would plant less wheat, but domestic consumption would go up,” Hayes said. “The lower supply would lead to higher global wheat prices, which tend to benefit wheat exporting countries including the United States.”
The study also indicated that with such changes, wheat trade flows would shift and the four countries would increase net imports by nearly 10 million metric tons (MMT). Hayes said the model estimated the United States would capture more than 20 percent of such an increase to export an additional 2.2 MMT compared to the model’s baseline if there were no changes in domestic support in those countries.
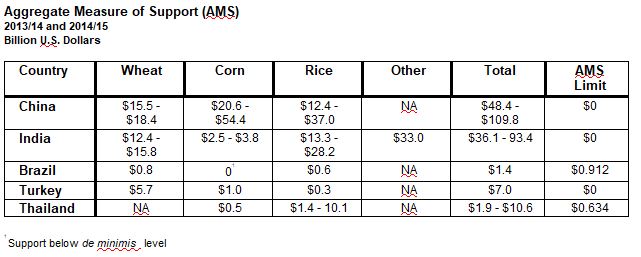
Hayes’ team also used the model to predict the net effect that eliminating support in individual countries would have (See Table 1). Those results indicated that domestic support for Chinese wheat production alone has the largest individual effect. If support there ended, Chinese imports would grow from nearly 2 MMT per year to more than 7.5 MMT per year. This would still be less than the 9 MMT annual tariff rate quota that China agreed to in its WTO accession commitments. Hayes said the model showed that even with the predicted changes, China, India, and Turkey would continue to be at least 90 percent self-sufficient in wheat production. Eliminating domestic support would have the least effect in Brazil where support levels are lower than the other countries.
Shifting the Narrative
Hayes also noted that this study compares future scenarios to data from a market situation in which wheat cash prices were significantly higher than they are now. For example, in addition to Chinese government input subsidies coupled to wheat production, the DTB Associates study in 2014 showed Chinese farmers have government minimum support prices of more than $10.00 per bushel.
“Wheat prices have plummeted more than 30 percent since last year, a significant portion of which is due to these countries’ market distorting policies, which send the wrong signals to their farmers. This hurts American family farms like mine even more,” said Brett Blankenship, who grows soft white wheat near Washtucna, Wash., and is the current President of the National Association of Wheat Growers (NAWG).
Referring to current negotiations in the Doha round, Blankenship added, “It is totally unacceptable to tolerate demands from countries who are in violation of their WTO commitments, who continue with these huge levels of support while demanding concessions from the United States. The American wheat farmer will not give away any more.”
WTO records show that the United States has consistently met its commitments, never exceeding its Aggregate Measure of Support (AMS) limit of $19.1 billion. But other country’s proposals made as part of the Doha round would require the United States to drastically cut its limit, while members with growing programs would not be expected to make meaningful contributions. Deputy U.S. Trade Representative Amb. Michael Punke has called this a “mind-boggling imbalance” that firmly underpins the U.S. position that it is critical to put facts on the table for a frank discussion about the real dynamic of world agricultural production and trade.
The new study indicated that wheat farmers outside of the four countries analyzed would benefit by reducing domestic supports. Hayes said the model showed global wheat cash prices would increase by more than four percent and world net trade would increase by five percent if domestic support is removed in all four countries. The study suggested that there would be benefits even from partial changes in price supports and input subsidies, although Hayes said the magnitude of the cash price and trade increase would depend on the size of the removal in each country.
“Since these subsidies are the acts of sovereign governments, our farmers cannot battle them alone. We are working with USTR and USDA to determine our next steps, including a possible WTO challenge,” Tracy concluded.
USW and NAWG have posted the entire report online at www.uswheat.org/policy and https://www.wheatworld.org/issues/trade/. Results of the two DTB Associates studies measuring domestic support in advanced developing countries, visit www.dtbassociates.com/docs/DomesticSupportStudy11-2014.pdf and www.dtbassociates.com/docs/domesticsupportstudy.pdf. For a third party analysis of individual policy measures by country, visit https://www.oecd.org/tad/agricultural-policies/producerandconsumersupportestimatesdatabase.htm#country.
USW is the wheat industry’s export market development organization working to promote all six classes of U.S. wheat in more than 100 countries. Its activities are made possible through producer checkoff dollars managed by 19 state wheat commissions and cost-share funding provided by USDA’s Foreign Agricultural Service. For more information, visit our website at www.uswheat.org.
NAWG is a federation of 22 state wheat grower associations that works to represent the needs and interests of wheat producers before Congress and federal agencies. Based in Washington, D.C., NAWG is grower-governed and grower-funded, and works in areas as diverse as federal farm policy, trade, environmental regulation, agricultural research and sustainability.
# # #
Nondiscrimination and Alternate Means of Communications
U.S. Wheat Associates prohibits discrimination in all its programs and activities on the basis of race, color, religion, national origin, gender, marital or family status, age, disability, political beliefs or sexual orientation. Persons with disabilities who require alternative means for communication of program information (Braille, large print, audiotape, etc.) should contact U.S. Wheat Associates at 202-463-0999 (TDD/TTY – 800-877-8339, or from outside the U.S.- 605-331-4923). To file a complaint of discrimination, write to Vice President of Finance, U.S. Wheat Associates, 3103 10th Street, North, Arlington, VA 22201, or call 202-463-0999. U.S. Wheat Associates is an equal opportunity provider and employer.