U.S. Wheat Associates (USW) participated in a Feb. 6 briefing panel for Capitol Hill staff that was focused on international food assistance programs and hosted by U.S. Representatives Tracey Mann (KS), Rick Crawford (AR), John Garamendi (CA) and Jimmy Panetta (CA).
USW Director of Trade Policy Peter Laudeman was a panel member along with representatives of rice and milling industry and the Seafarer’s Union (AFL-CIO). Rep. Mann moderated the discussion, while Rep. Crawford was on hand to remark on issues involving food programs.

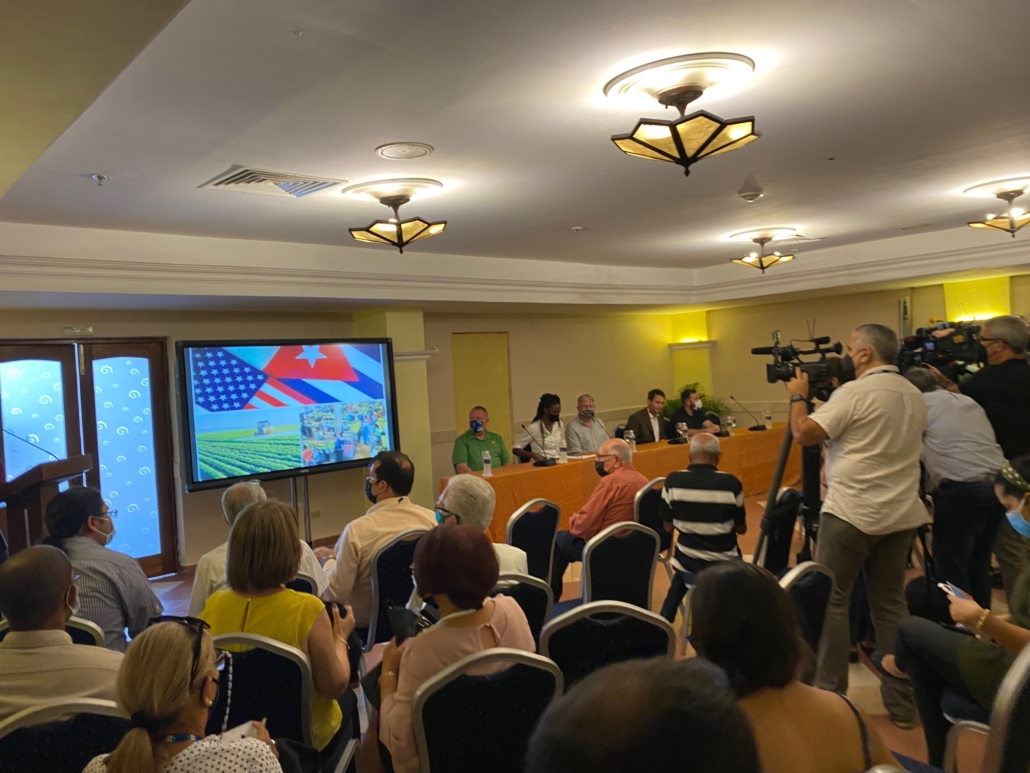
The panel that discussed food assistance programs for Capitol Hill staffers on Feb. 7 were (left to right): Bobby Hanks, representing USA Rive; USW Director of Trade Policy Peter Laudeman; Adam Thomas, representing the North American Millers’ Association; and Brian Schoenman, Political and Legislative Director of Seafarers International Union of North America.
A Team Effort
Joining Laudeman on the panel were Bobby Hanks, representing USA Rice; Adam Thomas, representing the North American Millers’ Association; and Brian Schoenman, Political and Legislative Director of Seafarers International Union of North America.
“The briefing covered a broad landscape but was particularly focused on the American Farmers Feed the World Act, which remains a strong opportunity to reinforce the role of U.S. commodities – most notably wheat – in international food assistance,” Laudeman said, noting that the legislation carries impact for both U.S. wheat producers and the entire wheat industry.
Part of Farm Bill Effort
The American Farmers Feed the World Act of 2023 would restore the emphasis on U.S.-grown commodities to fight global hunger, rather than using American taxpayers’ dollars to purchase food from America’s competitors. It would also restore transparency by reducing overhead costs, preserving resources to purchase life-saving food, and protecting at least 50% of the budget for purchasing U.S.-grown commodities and delivering them to the destination country.
“As both the House and Senate move closer to final Farm Bill text in each chamber, solidifying all additional support for the American Farmers Feed the World Act will be critical,” Laudeman added.
Wheat Plays Major Role
USW has joined the National Association of Wheat Growers (NAWG) and other agriculture commodity groups in backing the legislation since it was introduced in June 2023.
“America’s international food aid programs have enjoyed bipartisan support for more than 65 years because they are simple, effective, and they feed millions of vulnerable people around the world each year,” Mann said when introducing the Act in June 2023. “Through these programs, America fortifies our allies, counters the influence of foreign adversaries, creates new markets and trading partners, and stops wars before they start. For decades, America has purchased and donated American-grown commodities to execute our foreign assistance programs.”