By Elizabeth Westendorf, USW Assistant Director of Policy
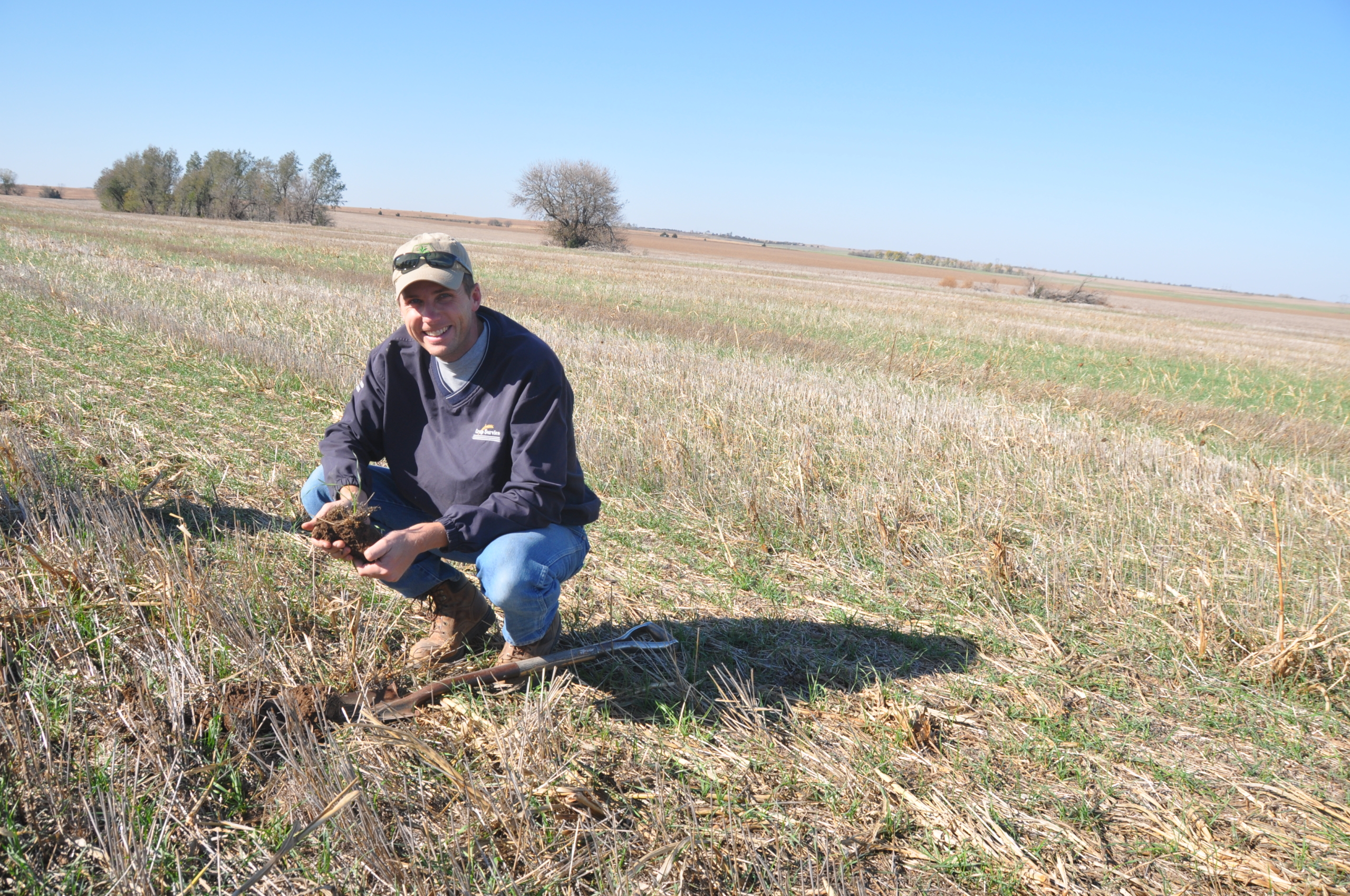
Justin Knopf’s family has been farming land in central Kansas for five generations — starting with their original homestead in the 1860s. Now, Knopf farms 4,000 acres with his father and brother, growing HRW wheat, alfalfa, grain sorghum, soybeans and corn.
“I feel like I have been given a gift to be able to work with the land, and that comes with responsibility,” said Knopf. “What I do impacts consumers, so it is important to take time and energy to be transparent with them and share the bigger story of what is happening in our landscape.”
Knopf is the last farmer in USW’s six-part series on farmer sustainability. USW has featured farmers from each class of U.S. wheat and from all over the country to highlight how their production practices are dependent on local factors and how they each address the goal of sustainability on their farm.
To Knopf, sustainability involves stewardship of resources in three areas — environmental, economic and human. He uses tools, research and continuing farm education opportunities to implement agronomic practices to protect natural resources such as soil, water and air, while also optimizing his production per unit of resources. This is environmental sustainability. Knopf also works to make economically responsible decisions for the farm because if it cannot survive as a business, he will not have a long-term ability to positively affect the environment down the road, which is economic sustainability. And finally, Knopf feels there is a human element to the sustainability conversation. He spends time focusing on the health and happiness of his family, his town and his neighbors while also working to educate consumers, which is social sustainability. All three of these are necessary for agriculture to thrive.
“The land will go on for much longer than I will be here, and it’s a much bigger story outside of myself, so I feel a responsibility to share that bigger story of what is happening with other people as a part of our stewardship,” said Knopf.
Knopf works to share his story by being involved in consumer outreach programs and sustainability research. Two years ago, in a partnership with Kansas Farm Bureau, he hosted a family on his farm for the day to show them how wheat is produced. Last year, Knopf was featured in the book “Rancher, Farmer, Fisherman: Conservation Heroes of the American Heartland” by Miriam Horn, which talked about his focus on improving soil health on his farm. A documentary film by the same title, narrated by award-winning journalist Tom Brokaw, and directed by Emmy-winning and Oscar-nominated Susan Froemke and Emmy-winning filmmaker John Hoffman, will premiere on the Discovery Channel in late August 2016.
Knopf’s emphasis on soil quality and increasing organic matter is particularly impressive. He does this by using no-till methods, carefully calibrating his crop rotations to maximize organic matter and experimenting with cover crops. These practices have improved his soil health, increased soil moisture and improved fertility, allowing him to reduce inputs like fertilizer and fuel and ultimately increase yields. As part of this constant effort to improve, Knopf experiments with new ideas on his farm to make sure that he is being a responsible land owner and manager.
“We see our soils as a fundamentally essential natural resource that is irreplaceable — and it takes a long time to build that soil up again if you lose it,” said Knopf. “And one of the foundational ideas of our family and our farm business is to be a steward of those natural resources and do everything we can to leave them in a better shape for the next generation.”
Learn more about Knopf and his farm at www.uswheat.org/factsheets. U.S. farmers, ranchers, fishermen and foresters also share their values, sustainability experiences and conservation practices at the U.S. Sustainability Alliance.