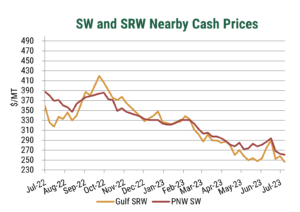
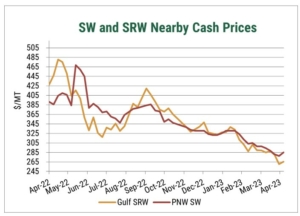
Drought in major U.S. wheat-growing regions over the past few years is well-documented. The persistent dry conditions acutely impacted U.S. wheat yield and increased abandonment, with 2023/24 production coming in 6% below the pre-drought five-year average. Now, entering the second half of the marketing year, the focus has shifted to the 2024 harvest and its impact on both U.S. and global supply and demand. Although it is early, optimism has begun to bloom for the 2024 winter wheat harvest, and the following highlights the factors that have helped boost the U.S. wheat outlook.
Acreage Down, But Conditions Improved
The Winter Wheat and Canola Seedings Report, published on Jan. 12, put the preliminary winter wheat acreage at 34.4 million acres (m.a.) (34.3 million hectares), down 6% from 2023 but still 4% ahead of the five-year average. The hard red winter (HRW) wheat area is estimated at 24.0 m.a. (9.7 million hectares), down 5% on the year, while the soft red winter (SRW) area is approximately 6.89 m.a. (2.8 million hectares), a 7% decrease. The white winter wheat (including soft white and hard white winter) area came in at 3.5 m.a. (1.4 million hectares). Desert Durum® seedings in Arizona and California for the 2024 harvest are estimated at 65,000 acres (26,300 hectares) total, up 16% from 2023 and 48% below 2022.
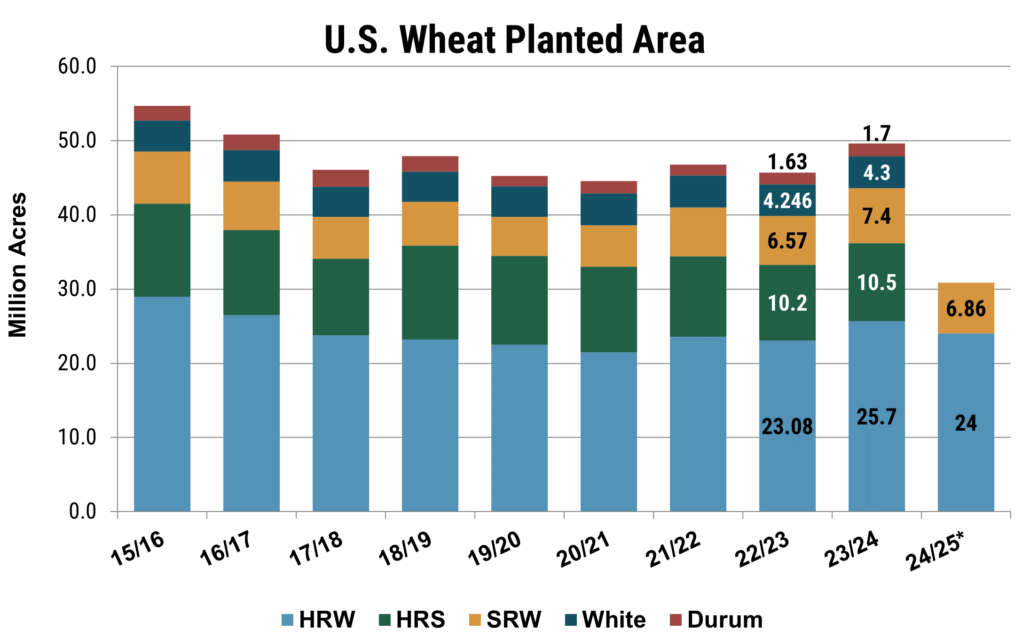
According to the Winter Wheat and Canola Seedings Report, published on Jan. 12, the winter wheat acreage is estimated at 34.4 m.a., down 6% from 2023 but still 4% ahead of the five-year average. The HRW area is estimated at 24.0 m.a., SRW at 6.89 ma, and the white winter wheat area came in at 3.5 m.a. Desert Durum® seedings in Arizona and California are estimated at a combined 65,000 acres. Source: USDA Winter Wheat and Canola Seedings Report.
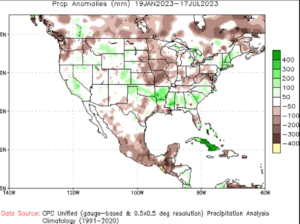
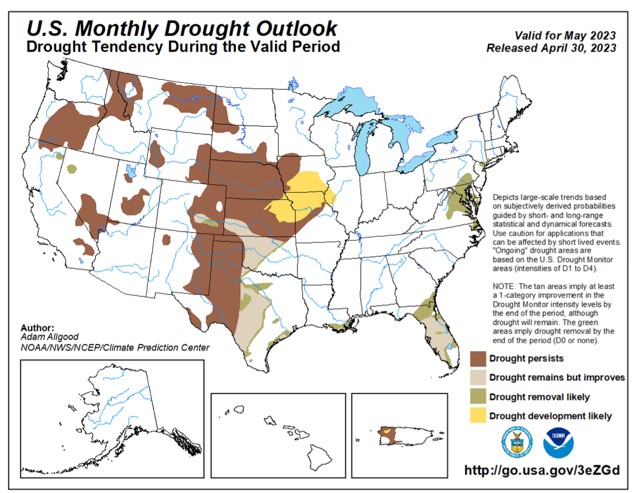
Moving toward fall of 2023, moisture helped replenish dry soil in the U.S. Southern Plains, aided planting, and supported early-season growth and emergence, while making visible improvements in the U.S. Drought Monitor. According to USDA, as of Jan. 30, 2024, winter wheat area in drought registered at 17%, down from 22% the week prior and 58% last year. Meanwhile, the last aggregate USDA Crop Progress Report, published on Nov. 27, 2023, put 50% of winter wheat in the good to excellent category, the highest since 2020.
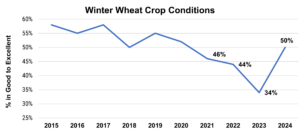
The last national USDA Crop Progress Report put 50% of the U.S. winter wheat crop in good to excellent condition, the highest since 2020. Source: USDA NASS Data.
Despite the decreased acreage, the cautious optimism about wheat conditions suggests the potential for improved yield and reduced abandonment for the 2024 harvest. Improved yields will provide a welcome boost to U.S. wheat production, helping improve supply and relieving pressure on the U.S. balance sheet and wheat prices.
An Early State-by-State Snapshot
Comments from producers at a recent meeting of the U.S. Wheat Associates (USW) Wheat Quality Committee echoed the optimistic sentiment. However, despite the objectively improved crop outlook from the year prior, winter conditions have started to vary as the season progresses, serving as a reminder that much can change before harvest time.
Following are condition recaps in major winter wheat-producing states from committee members and National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS) data as of Jan. 28:
Kansas. Data from NASS rates 54% of Kansas winter wheat good to excellent, and optimism has bloomed regarding the 2024 harvest. Kansas wheat farmer and USW Secretary-Treasurer elect Gary Millershaski highlighted visible improvements to wheat stands compared to the previous year.
Texas. NASS data put Texas wheat conditions at 42% good to excellent, while Texas farmers remain optimistic about current conditions.
Oklahoma. An Oklahoma farmer commented that soil moisture remains adequate, and the wheat entered dormancy in good condition. Oklahoma crop conditions rated 63% of the crop in the good to excellent category.
Colorado. About 61% of the crop sits in the good to excellent category, though winds and dry weather this winter may cause some condition deterioration.
Nebraska. According to a Nebraska farmer, rain during planting helped boost conditions, and the stands continue to benefit from the soil moisture. Current conditions put Nebraska winter wheat at 69% good to excellent.
South Dakota. South Dakota Wheat Commission CEO Jon Kleinjan commented that the state’s HRW wheat was seeded with adequate moisture. As good snow cover remains, he is optimistic about the 2024 crop. Likewise, NASS put 53% of winter wheat in good to excellent.
Montana. Approximately 41% of the HRW crop sits in the good category; however, cold and a lack of snow coverage have negatively impacted crop conditions this winter.
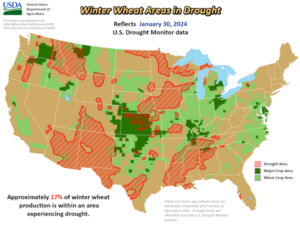
According to the weekly USDA Agriculture in Drought Report, as of Jan. 30, 2024, 17% of U.S. winter wheat resides in areas experiencing drought, down from 22% last week and much improved from 58% last year. Source: U.S. Agriculture in Drought.
More Data to Come
The upcoming USDA Prospective Plantings Report will provide preliminary estimates for spring wheat, durum, and the white spring wheat area and update the winter wheat estimates. It is important to remember that the 2024 harvest is still months away, and conditions can and will change as the crop year progresses. Nonetheless, even after an extended drought, U.S. wheat farmers remain resilient and committed to growing a reliable supply of high-quality wheat for their customers around the world.
By USW Market Analyst Tyllor Ledford