Breads made with U.S. wheat caught the attention of the U.S. Ambassador to Chile during September’s Espacio Food and Service trade show in Santiago. It set in motion a series of discussions that led to Amb. Bernadette Meehan touring a top Chilean flour mill arranged by the U.S. Wheat Associates (USW) South American regional team.
The bread Meehan raved about at the show was baked in the USW wheat flour and baking laboratory on the campus of Universidad Mayor.
“Ambassador Meehan opened the Food and Service Show this past fall and noted an interest in the bread at our display. She wanted to know more about U.S. wheat’s work in Chile, the flour milling process and the products produced using U.S. wheat,” explained Miguel Galdos, USW Regional Director in South America. “I contacted a USDA Foreign Agricultural Service (FAS) specialist and set up a visit to a mill. We met and toured a mill on Jan. 10 at Molinos Cunaco, a customer of U.S. wheat and one of Chile’s largest milling companies.”
Molinos Cunaco processes approximately 300,000 metric tons of wheat each year, of which 30% to 35% is U.S. wheat.
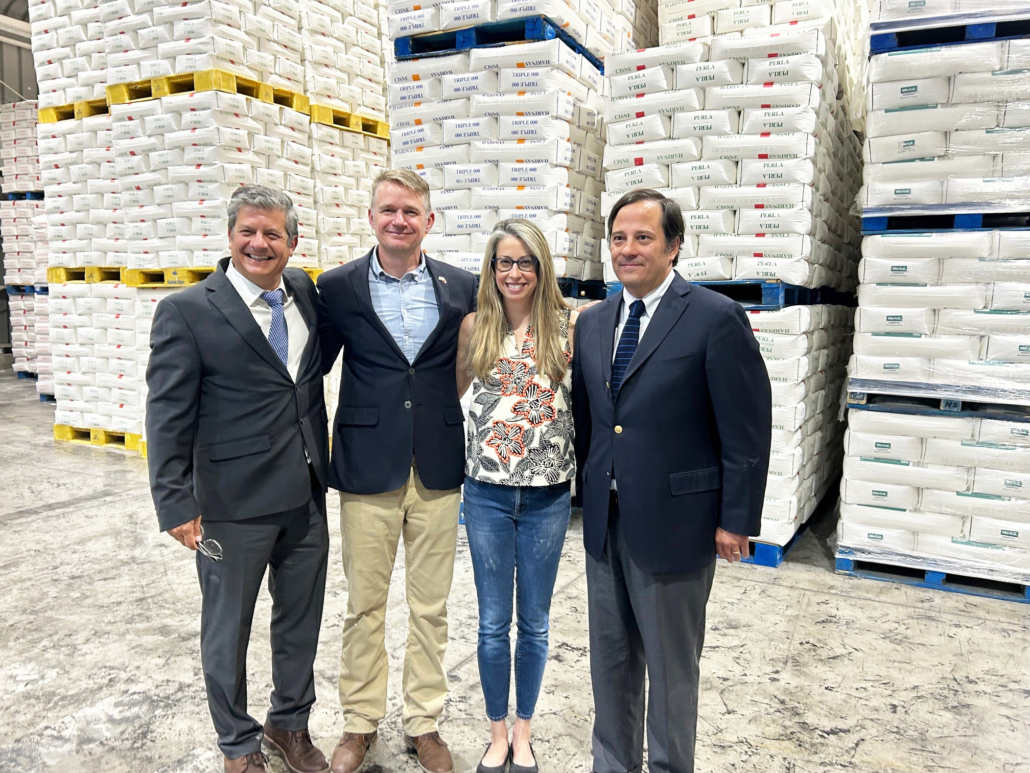

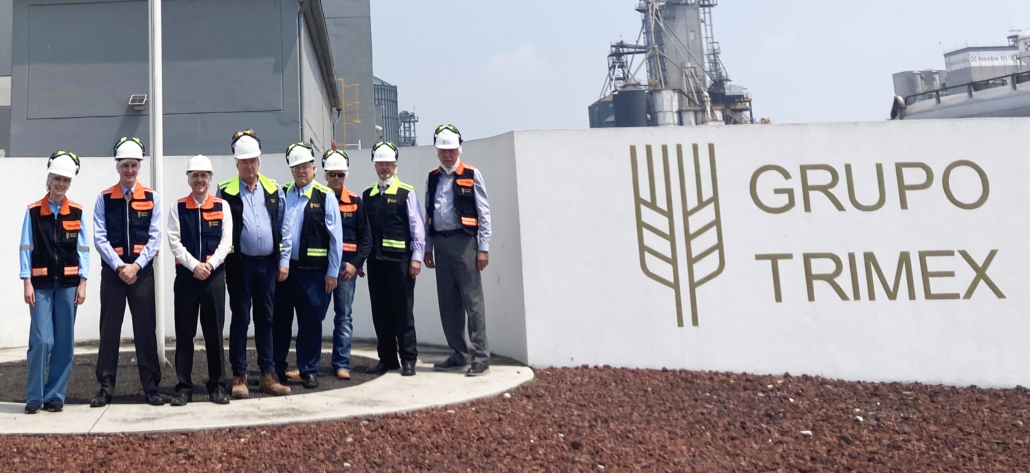
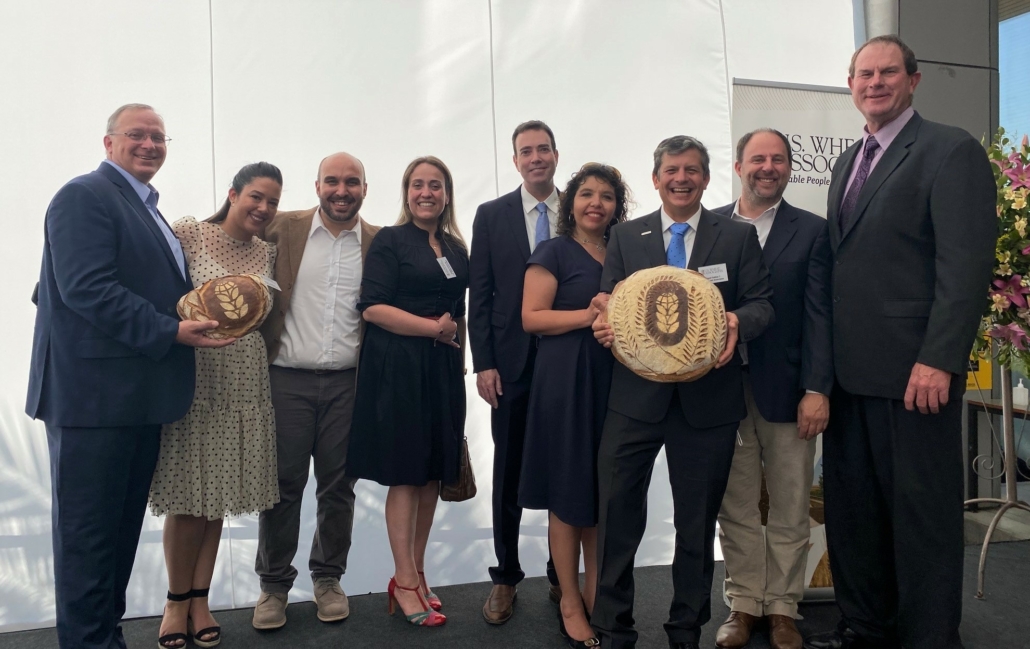
USW arranged a tour of a Molinos Cunaco flour mill for U.S. Ambassador to Chile Bernadette Meehan. Posing for a photo in the mill’s packaging department are (left to right) USW Regional Director Miguel Galdos, U.S. Agricultural Attaché Bret Tate, Ambassador Meehan, and Molinos Cunaco General Manager Cristian Diaz.
A Close Look at U.S. Wheat in the Market
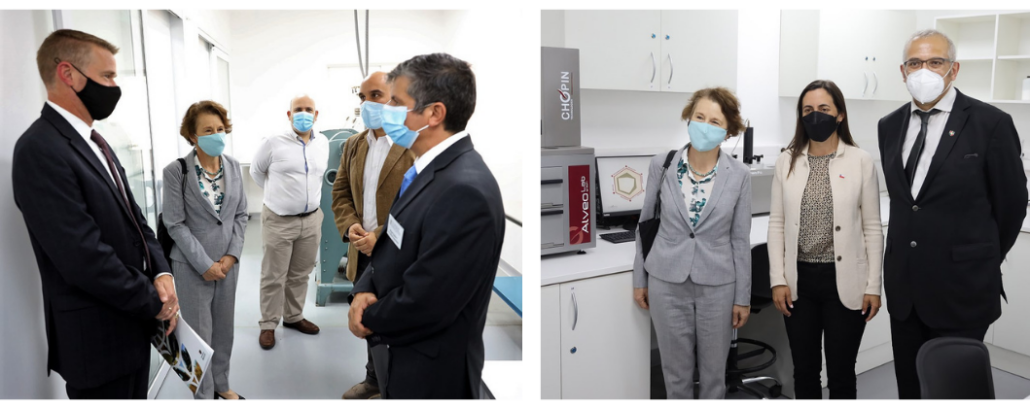
Meehan became Ambassador to Chile in July 2022. She was joined on the mill tour by U.S. Agricultural Attaché Bret Tate and FAS Marketing Specialist Maria Jose Herrera. Molinos Cunaco’s General Manager Cristian Díaz, Director Juan Enrique Ojeda and Finance Manager José Ignacio Vargas hosted the American group.
“The meeting between the Ambassador and the executives covered a lot of topics,” Galdos reported. “One topic was the current situation of the milling industry in Chile. They also discussed the commercial relationship between the company and its wheat suppliers. Cooperation of the U.S. government on issues involving Chilean agriculture and trade was also part of the chat.”
After the meeting, the group moved to the mill. Meehan walked all five floors of the facility to see the entire milling process – from U.S. wheat being brought into the mill to the department where flour made with the wheat is packaged.

Galdos shares a U.S. wheat sample card with ambassador Meehan during discussions about the many uses for U.S. wheat and the preferences of end users in Chile.
Chile Typically Imports Four Classes of Wheat
Galdos shared with her the fact that U.S. wheat currently has about a 30% market share in Chile. He explained that Chile typically imports four classes of U.S. wheat: hard red winter, soft red winter, soft white and hard red spring wheat. In 2023, due to the pricing situation, only three classes were purchased by Chilean millers – soft white, soft red winter and hard red winter.
“The ambassador asked a lot of questions about wheat, the milling process and the end products. We answered all of her questions,” said Galdos. “She had the opportunity to meet the people who work in different areas of the company.”
Ambassador Shares Appreciation for USW
Later that day, Meehan posted an account of the tour on her X, formerly Twitter, account, which can be seen here.
“Incredible experience today at #molinocunaco with representatives from U.S. Wheat Associates,” Meehan noted in her post. “I discovered that Chile imports American wheat varieties for bread and other high-quality delicacies – continued collaboration to deliver exceptional products to consumers.”