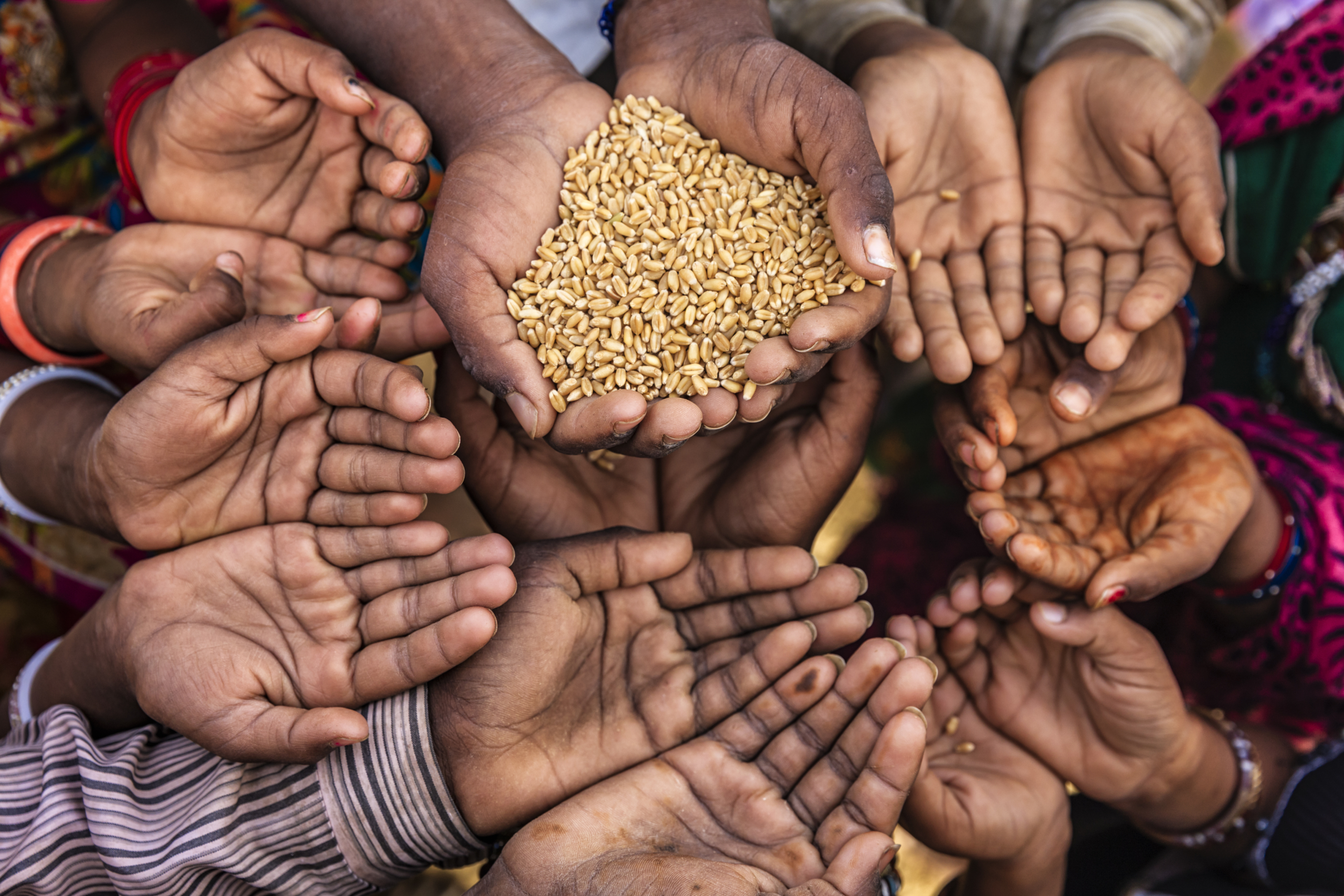
The United States sends more international food aid to those in need than any other country. U.S. food aid programs are managed by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) or the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and include either commodity, cash or food voucher donations. U.S. wheat is typically the commodity utilized the most through in-kind donations.
U.S. Food Aid Programs
The USDA Foreign Agricultural Service (FAS) coordinates the Food for Progress program, which prioritizes countries in need annually. Through the program, the USDA purchases U.S. commodities to donate to priority developing countries where the commodity is sold to support agricultural development projects in those countries.
However, most U.S. food aid is operated by USAID’s Food for Peace office. Title II of the Food for Peace Act is primarily an emergency food assistance program. USAID purchases commodities for Title II from the United States at market price and donates them to meet the immediate nutritional needs of those facing hunger. In other cases, USAID will purchase and donate local or regionally grown commodities or provide market-based food vouchers and cash. The type of assistance varies based on local circumstances and needs.
Currently, the two largest recipients of wheat under the Food for Peace program are Ethiopia and Yemen. Ethiopia receives U.S. hard red winter (HRW) wheat, while Yemen receives U.S. soft white (SW) wheat, as these two wheat classes best meet the local demand.
USAID programs using SW wheat are most important to the Pacific Northwest, including Idaho. Wheat donations to Yemen represent approximately 30% of all U.S. wheat food aid donations. Although supplies have been tight for marketing year 2021/22 due to weather, the Pacific Northwest has remained a consistent supplier of food aid to Yemen when it is most in need.
Challenges
Under USAID’s food aid programs, cash and vouchers represent most of the aid provided, surpassing in-kind commodity donations in recent years, which account for 40% of aid. USAID’s justification for this preference is that supplying cash and vouchers is more cost-efficient than shipping commodities.
This leads to another challenge in the U.S. food aid programs. Cargo preference policies currently require that 50% of food aid be shipped on U.S.-flagged vessels, imposing additional costs on these programs. A study from the Government Accountability Office (GAO) states that cargo preference requirements on shipping commodities for food aid increased costs by about 23%, or $107 million, from 2011 to 2014.
As a result, this requirement limits the amount of funding spent on purchasing U.S. commodities and reduces the amount of food aid that reaches those most in need. However, the costs of cargo preference policies were once offset by a reimbursement program from the maritime administration. This allowed the benefit of maintaining a U.S.-flagged vessel fleet for the maritime industry while keeping more funding in USDA and USAID food aid programs. With the elimination of these reimbursements, the additional costs impact the amount of commodities purchased for food aid programs.
Today’s Crisis and Tighter Wheat Supplies
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine started a ripple effect of catastrophic events in the Black Sea region. The unjust attack on Ukraine and its people has increased the risk of food insecurity globally as many countries heavily rely on low-cost wheat from this region. Ports along the Black Sea in Ukraine have remained closed due to these needless attacks, although Russia has continued to export. With Ukrainian ports closed, some European countries, notably Romania, have been helping Ukraine export its grain through its ports.
The Black Sea region supplies around 30% of the world’s wheat exports. Many countries that depend on this region to meet their wheat demand are questioning where they can import wheat from while facing significantly higher costs. The European Union, United States, Canada and Australia are expected to pick up much of the demand but with limits. Although India increased its exports at the start of the crisis, helping meet global demands, India recently announced it would restrict wheat exports over concerns domestic wheat production will not be as high.
The U.S. Wheat Industry’s Commitment
As food costs continue to rise, the impact of a global pandemic continues, and now a war in an important wheat production region will likely push more people into food insecurity across the globe. U.S. Wheat Associates (USW) and the Food Aid Working Group (FAWG), a joint working group between USW and the National Association of Wheat Growers (NAWG), are proud of the wheat provided through these food aid programs and believe that commodities should be kept in these programs. The U.S. wheat industry is committed to food assistance that impacts the most vulnerable populations to provide food security.
By Shelbi Knisley, USW Director of Policy








 Virtual meetings with officials this year focused on two major challenges: a rising trend toward using larger amounts of cash and vouchers in food aid programs; and cargo preference shipping rules that increase the cost of U.S.-sourced wheat and other commodity donations.
Virtual meetings with officials this year focused on two major challenges: a rising trend toward using larger amounts of cash and vouchers in food aid programs; and cargo preference shipping rules that increase the cost of U.S.-sourced wheat and other commodity donations.