In the increasingly competitive global wheat market, it is important to review the advantages that U.S. wheat delivers to millers and bakers. This post examines the advantages that durum wheat brings to the market.
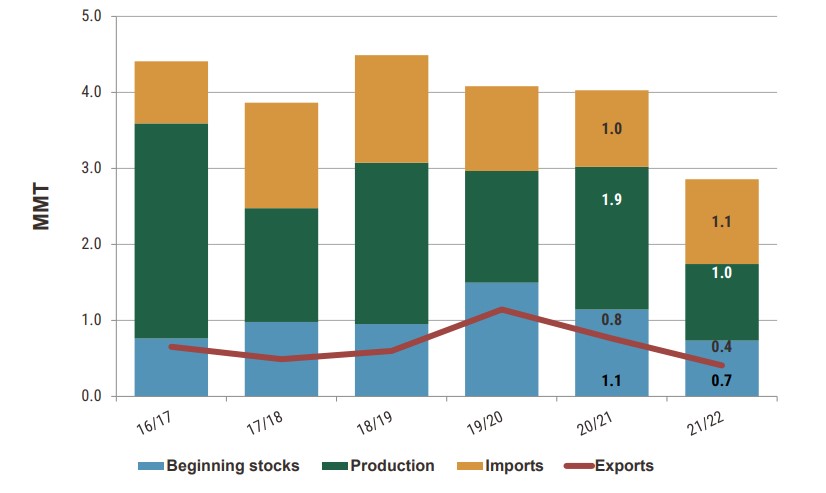
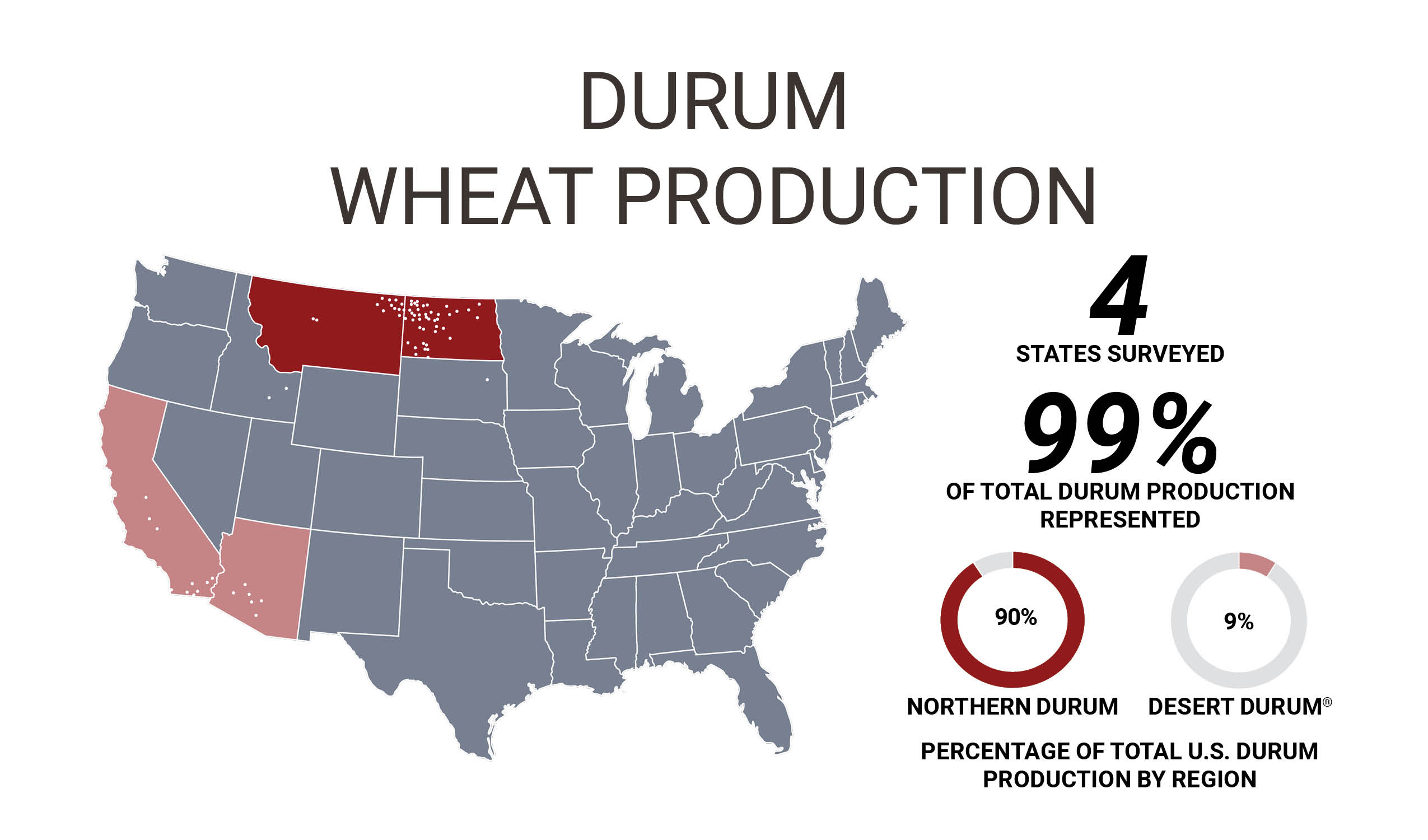
Durum is the pasta wheat and the fifth-largest class of wheat grown in the United States with an annual average production over the last five years of 1.6 million metric tons (MMT), or about 58.79 million bushels. In part because of regional economies of scale, U.S. imports of durum at a 5-year average are 1.18 million metric tons (MMT). In comparison, export volume at a 5-year average is slightly less than 680 thousand metric tons (TMT).
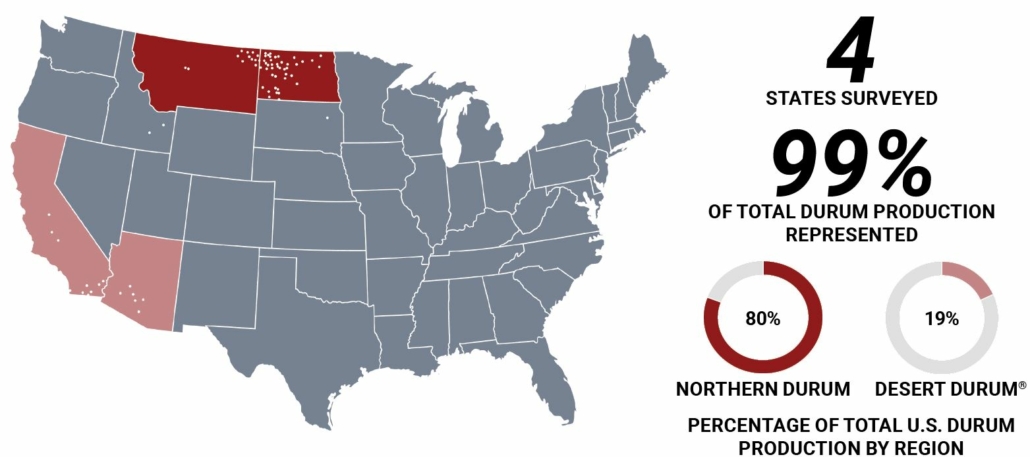
Northern durum is grown in North Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana and primarily exported through the Lakes via the St. Lawrence Seaway or the Gulf. Desert Durum® is a registered certification mark owned by the Arizona Grain Research and Promotion Council and the California Wheat Commission. These groups authorize using the mark only for designated durum grain produced under irrigation in Arizona and California’s desert valleys and lowlands. Desert Durum® is exported from the Gulf or the West Coast.

The finest quality pasta is produced from U.S. durum grown in the northern Plains and in the southwest as Desert Durum®.
Milling Advantages
U.S. durum is competitive mostly with Canadian durum in the global market. U.S. durum is represented by three subclasses controlling for hard, vitreous kernel (HVK) content. Subclass options include Hard Amber Durum (HAD) with more than 75% vitreous kernels; Amber Durum with 60% to 74% vitreous kernels; and Durum with less than 60% vitreous kernels. Higher HVK values yield a larger quantity of semolina. U.S. durum has a large kernel size, allowing millers to benefit from higher extraction rates.
Desert Durum® is harvested and shipped at a very low moisture content. This advantage to millers contributes to efficient transportation costs and high extraction rates. It also allows them to add significantly more water during the tempering and conditioning phase of processing.
Product Advantages
The finest quality pasta is the primary product made from U.S. durum – long goods, short goods, pasta of all shapes and sizes. Other products made from durum include couscous and some varieties of traditional Mediterranean semolina bread. In all durum food products, one quality factor is the most critical to the consumer – color. In its purest form, pasta is water and durum semolina. Couscous is large semolina boiled and eaten as an alternative to rice. In both products, consumers prefer a bright yellow, translucent appearance that U.S. durum delivers because of its higher HVK level. The higher HVK also allows the miller to provide a more uniform, consistent semolina to the pasta process, thus improving production efficiencies and color.
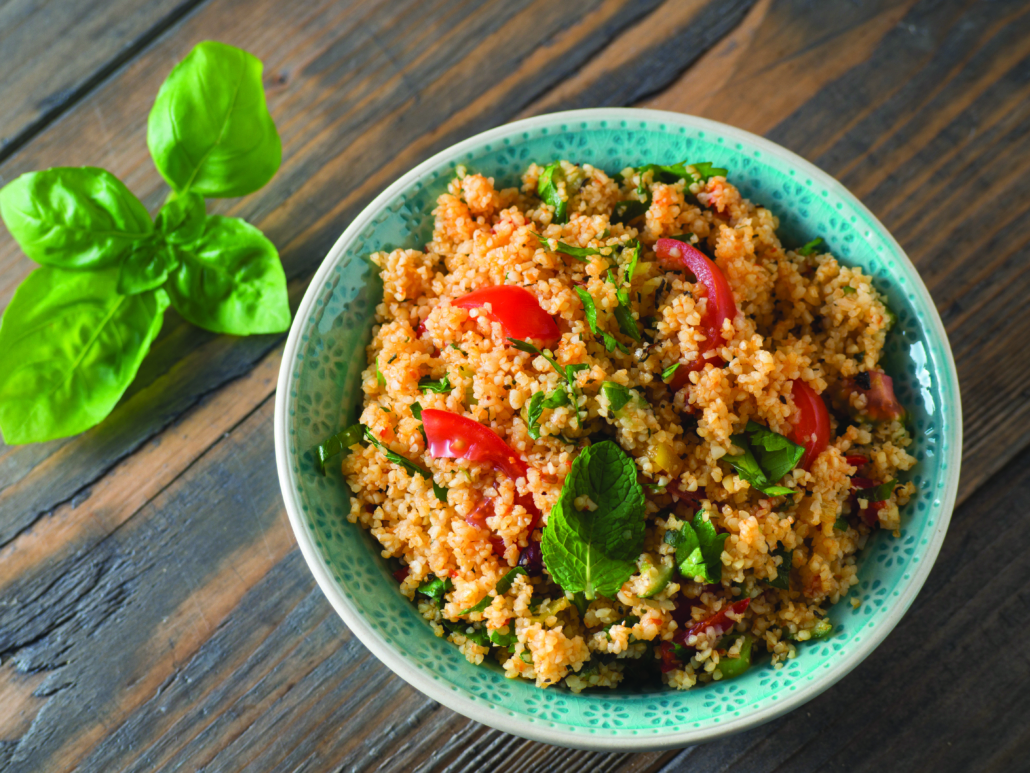

Couscous is produced with durum wheat.
Sourcing Opportunities
Like some other classes of wheat, U.S. durum planted area is declining. Proactively working with producers and suppliers is the best way to assure ample supply to the market. Desert Durum® can be produced and delivered “identity-preserved” to domestic and export markets, which allows customers to purchase grain of varieties possessing quality traits specific to their needs. Annual production requirements can be pre-contracted with grain merchandisers ahead of the fall-winter planting season for harvest from late May to early July. Varietal identity is maintained by experienced growers planting certified seed and merchandisers who store and ship according to customers’ preferred delivery schedules.
Northern durum is competitively sourced by U.S. pasta producers in the Midwest and northern states. Export customers must be proactive when working with suppliers to obtain the best quality available, such as HAD.
U.S. Wheat Advantages
As we highlight each specific class in this series, let us not forget the advantages that all U.S. wheat classes bring to the market. First, and perhaps the most important, is consistency in quality and consistency of supply. Although each new crop year brings different challenges and opportunities, U.S. wheat is always available to the global market. Second, U.S. wheat delivers variety. Wheat is a raw material manufactured into a bakery ingredient: flour. The flour made from each class of U.S. wheat brings value to the market through specific quality characteristics that make a variety of baked goods and noodles. Further, blending flours from one or more types of wheat is an important component for customers to understand as part of optimizing flour performance at a minimal cost.
Each region, country, and culture have wheat-based food products that are uniquely their own. With six unique wheat classes, the United States has the right wheat class to deliver the optimal quality and value for every variety of product on the market.
Learn more about the six classes of U.S. wheat here or leave a question in our “Ask The Expert” section.
By Mark Fowler, USW Vice President of Global Technical Services
Read more about other U.S. wheat classes in this series.
Hard Red Winter
Hard Red Spring
Hard White
Soft White
Soft Red Winter