By Stephanie Bryant-Erdmann, USW Market Analyst
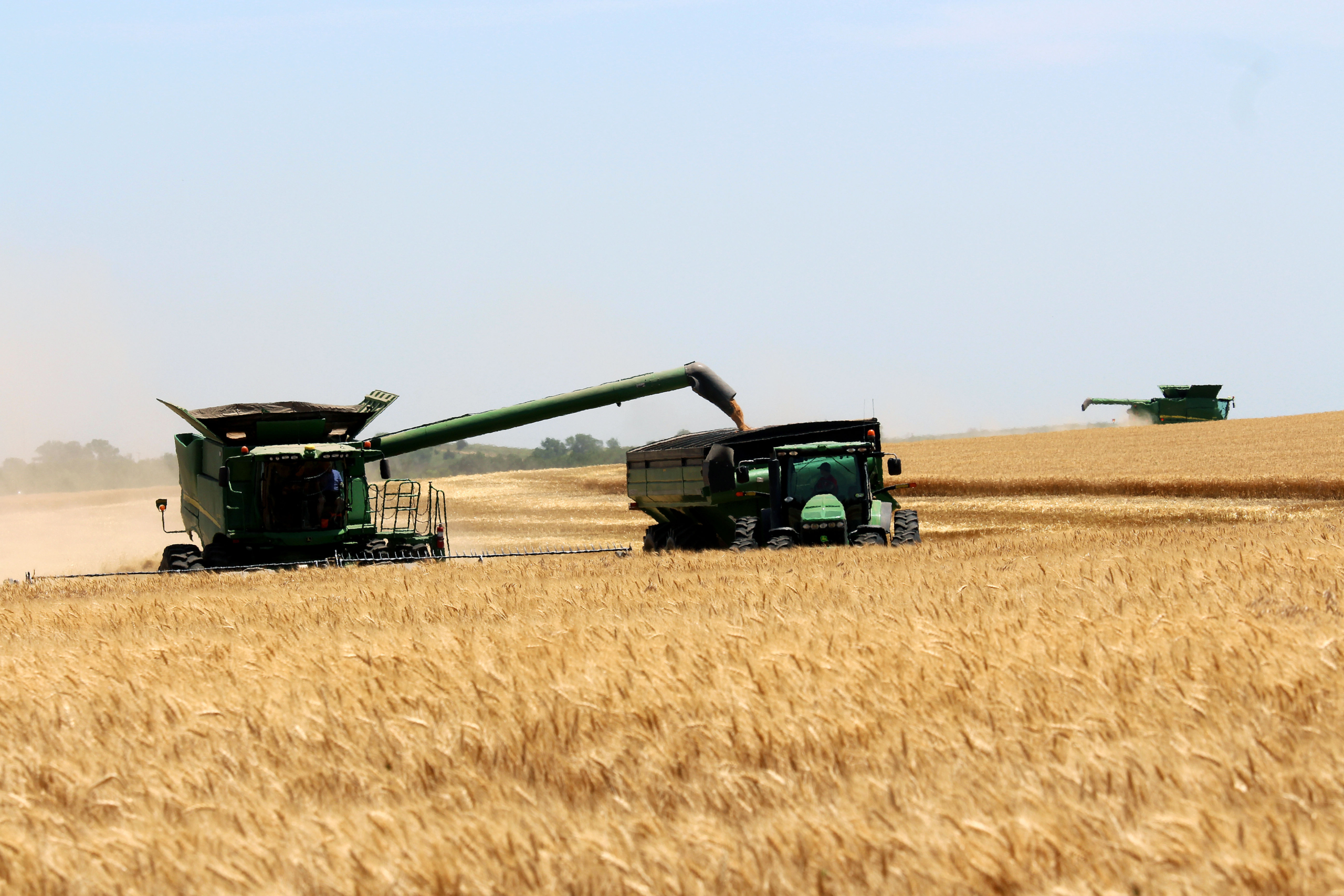
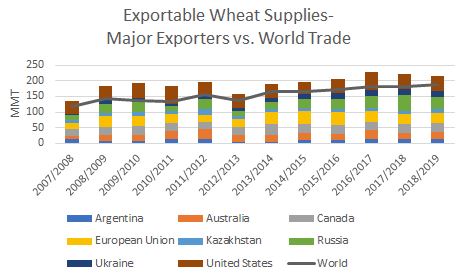
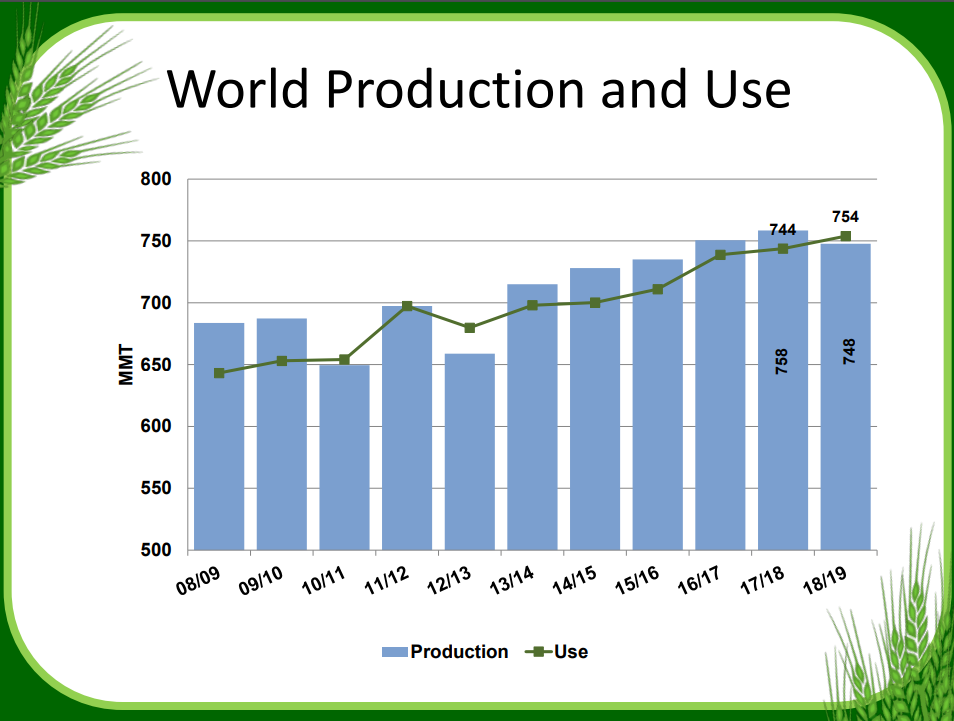
With the world consuming more wheat than it produces for the first year since 2012/13, prices are also on the rise. According to Global Trade Atlas data, the average global wheat price increased 4 percent year over year to $203 per metric ton (MT) in 2017/18 (June 1 to May 31). Most of that price increase occurred in the last five months of the marketing year as the market digested lower Northern Hemisphere wheat production estimates and strong demand for 2018/19.
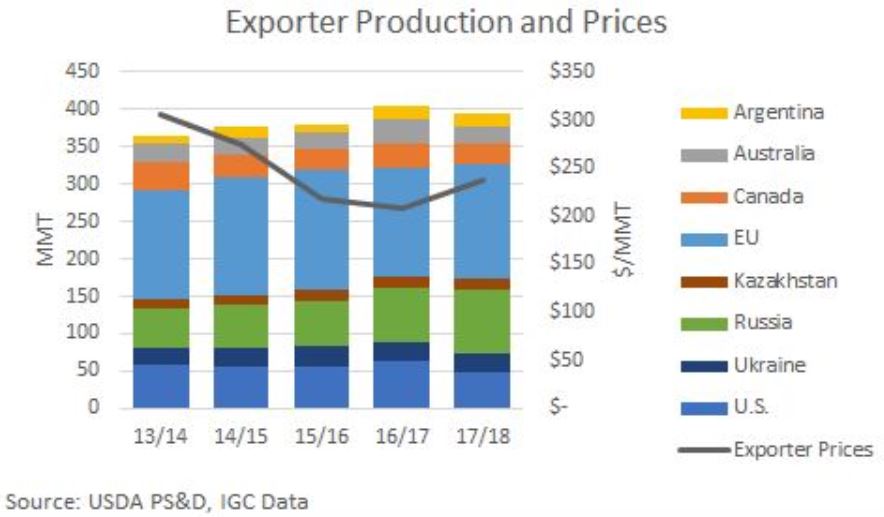
Here is a by-country look at current production estimates and the average wheat prices (noting that prices vary by class and quality) from major exporting countries and regions.
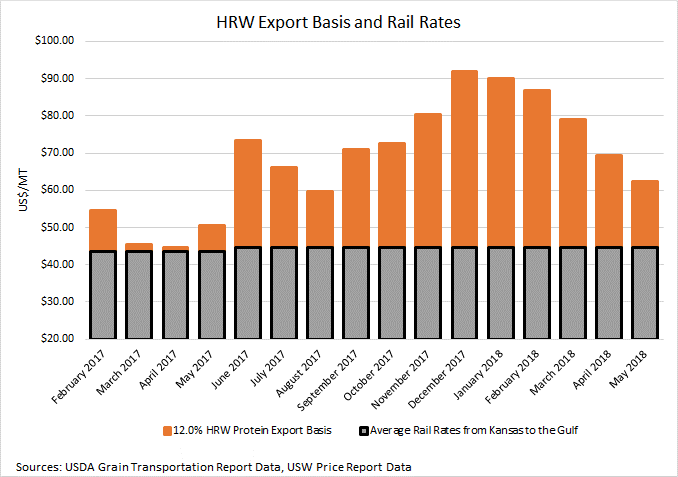
United States. According to the U.S. Wheat Associates Price Report, the average price for U.S. wheat rose an average $47 per MT from one year ago. Hot, dry conditions in the U.S. hard red winter (HRW) growing region decreased yield potential and pushed prices up for this largest U.S. wheat class. USDA forecasts U.S. 2018/19 wheat production at 49.7 million metric tons (MMT), up 5 percent year-over-year, but still 11 percent below the 5-year average. U.S. beginning stocks are estimated at 29.4 MMT, down 8 percent from 2017/18, but still 28 percent above the 5-year average. Increased U.S. wheat production is expected to offset the lower U.S. beginning stocks and total U.S. supply is expected to remain stable year over year at 79.1 MMT.
Canada. The International Grains Council (IGC) reported the average price for Canada Western Red Spring (CWRS) at 13.5 percent protein (13.5 percent moisture basis) from Vancouver rose to $255 per MT in May. This is up $24 per MT from May 2017 and reflects the tighter global supply and demand picture. On June 21, Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC) forecasted 2018/19 common wheat production (excluding durum) at 25.4 MMT, up slightly from 2017/18. A 15 percent bump in spring wheat planted area contrasts with an 11 percent drop in winter wheat planted area. Predicted 2018/19 durum production will increase 15 percent to 5.7 MMT due to an 11 percent year over year increase in planted area. The global supply and demand situation for durum wheat is also supporting prices. Canadian durum prices at $282 per MT are an average $7 per MT above 2017 levels.
European Union (EU). IGC reported the average French wheat price reached $205 per MT in May, up from $187 per MT the year prior. French production is expected to increase to 37.8 MMT, up 4 percent due to higher expected yield and larger planted area. 2018/19 EU wheat production is expected to fall 1.80 MMT from 2017/18 to 140 MMT according to Stratégie Grains, which is providing continued price support for exportable French supplies.
Australia. The current average price for Australian wheat of $239 per MT is up 22 percent year over year according to IGC data, which point to lower carry-in stocks and hot, dry conditions. In June, the Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics and Science (ABARES) forecasted 2018/19 Australian wheat production to rise 3 percent from 2017/18 to 21.9 MMT, despite a 3 percent decrease in planted area to 29.5 million acres (12.0 million hectares).
Argentina. In May, the average price for Argentine wheat reached $261 per MT according to IGC data. That is up 38 percent year over year. This month, the Buenos Aires Grain Exchange reported Argentine farmers see higher revenue potential and expects them to plant 7 percent more area to wheat in 2018/19, reaching 15.1 million acres (6.1 million hectares). USDA’s June estimate for 2018/19 Argentina’s wheat production was 19.5 MMT (716 million bushels), up 8 percent from 2017/18 and 35 percent greater than the 5-year average.
Black Sea (Russia, Ukraine and Kazakhstan). The average price for Russian 4th grade milling wheat (8.8 to 10.5 percent protein on a 12 percent moisture basis) reached $213 per MT in May, up 14 percent from the year prior according to IGC. Expectations for lower 2018/19 production in the Black Sea region are supporting export prices. USDA projects combined 2018/19 output from Russia, Ukraine and Kazakhstan will drop 14 percent to 109 MMT (4.00 billion bushels) based on an expected return to trendline yields. If realized, the combined harvest would still be greater than the 5-year average.
At the end of May, the Russian Meteorological Service noted hot, dry conditions threatened winter wheat in Russia’s southern regions, which have not received rain since April. Conversely, cold wet weather is delaying spring wheat planting in other regions. To date, 23.3 million acres (9.43 million hectares) of spring wheat has been planted, compared to the 2017/18 total spring wheat area of 30.9 million acres (12.5 million hectares). Russian consultancy SovEcon forecasted Russian wheat production to decline to 77.0 MMT (2.83 billion bushels), down 10 percent from 2017/18.
UkrAgroConsult reported Ukrainian wheat planted area increased 2 percent year over year to 15.5 million acres (6.28 million hectares). The Ukrainian meteorological service expects wheat yields to fall 8 percent year over year to 56.5 bu/acre (3.80 MT/ha). 2018/19 Ukrainian wheat production is forecast at 23.9 MMT (878 million bushels), compared to 25.4 MMT (933 million bushels) in 2017/18.
IGC expects yield declines and smaller planted area will lower Kazakhstan wheat production to 13.7 MMT (503 million bushels), down 7 percent from 2017/18, if realized.