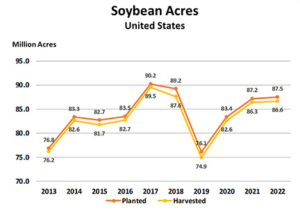
As the 2023/24 marketing year begins, the market awaits the outlook for the new crop harvest. Despite early concerns anticipating wet conditions and late planting similar to the 2022 crop year, hard red spring (HRS) planting progress has surpassed expectations.
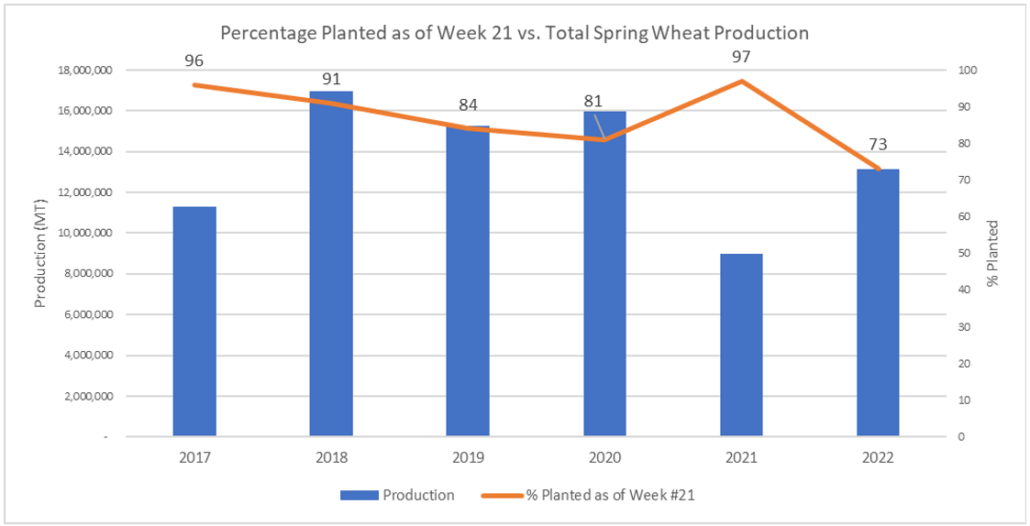
Though planting progress influences total production and yield, it is not predictive. Years with late planting can yield average crops, while rapid planting does not equate to good production potential. Factors such as soil moisture, weather, and disease pressure can significantly influence yield potential during crop development. Source: USDA NASS Data.
Rapid Planting Progress
Spring wheat farmers have made incredible planting progress after a historically snowy and cold winter delayed spring fieldwork in the Northern Plains. According to the USDA Crop Progress Report, as of June 4, 93% of the spring wheat was planted, up from 85% the week prior and even with the five-year average. In key HRS-producing states North Dakota, Montana, and Minnesota, USDA estimates plantings at 88%, 92%, and 98% complete, respectively. Over the last several weeks, rainfall has benefited soil moisture, and more recently, dry weather paired with above-normal temperatures helped accelerate planting progress. Between May 21 and May 28, 45% of the spring wheat crop was planted.
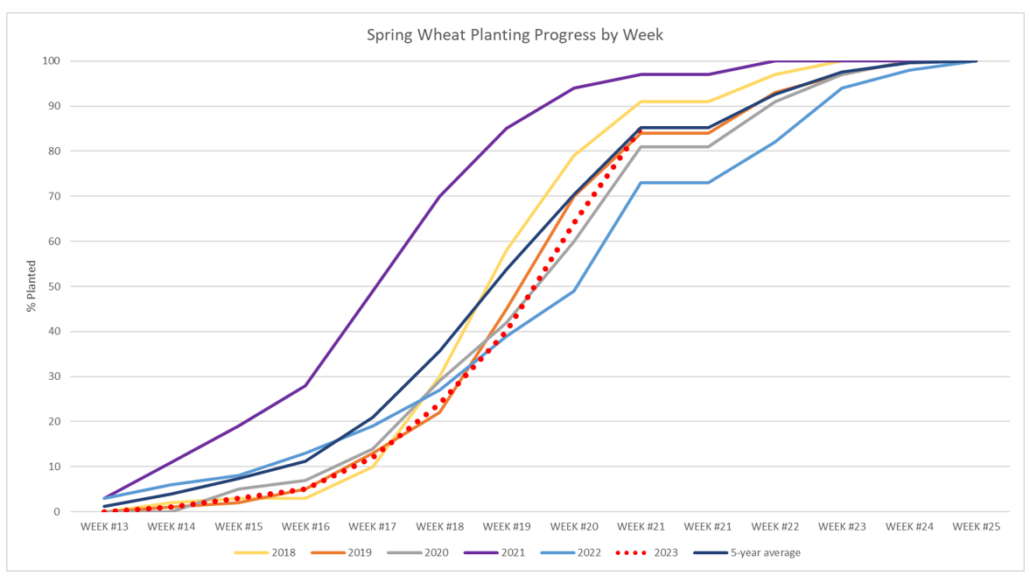
After a long winter with historic snowfall in the Northern Plains, 2023 planting (red dotted line) started late. As temperatures warmed rapidly, progress accelerated from several weeks behind to even with the five-year average. Source: USDA NASS Data.
A Hopeful Forecast
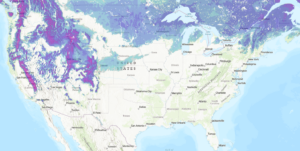
As spring wheat planting winds down, emergence hovers near the five-year average. As of June 4, spring wheat was 76% emerged, above the five-year average of 74%. The forecast predicts scattered showers for North Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana, a potential benefit to the newly planted HRS crop. Topsoil moisture in the top HRS producers remains good, with 72% boasting adequate to surplus moisture in North Dakota and 66% in Minnesota; meanwhile, drought removal is likely in much of Montana’s growing regions.
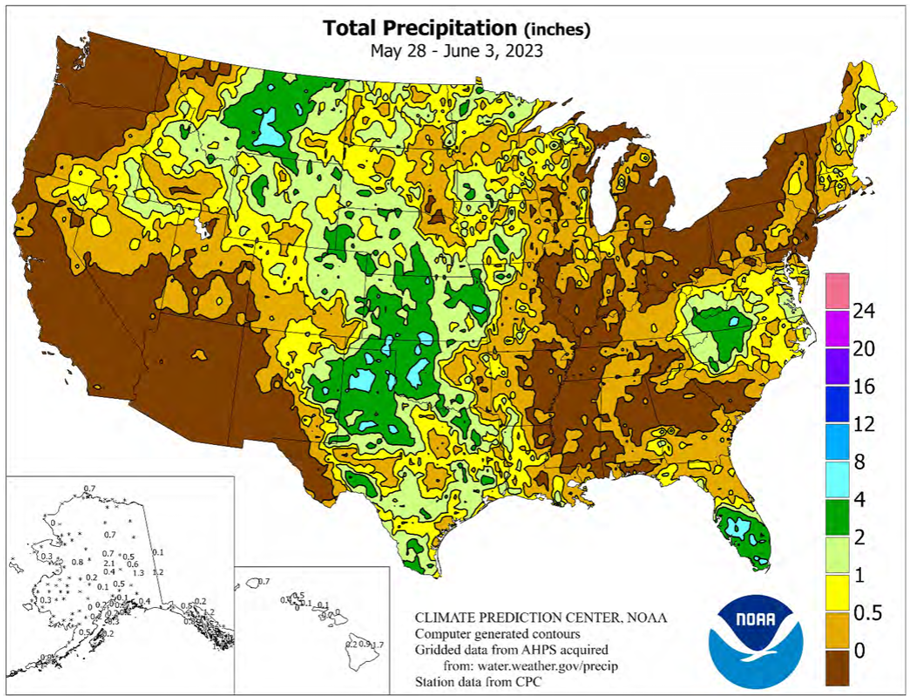
Scattered showers have greatly benefited much of the U.S. wheat-growing regions, alleviating Montana’s drought and improving conditions in other key producing states. Source: USDA Weekly Weather and Crop Bulletin.
Looking Ahead
The current outlook for HRS remains positive, though continued optimism hinges upon the weather’s cooperation. Recent warm temperatures helped jumpstart planting and emergence, but additional moisture will be necessary to sustain the current confidence levels.
In addition to weather, the underlying impacts of the tight HRS balance sheet and lingering price volatility due to the war in Ukraine will continue to influence the market. As the 2023/24 marketing year continues additional information regarding the production outlook will become available.
To be released on July 12, the July Crop Production Report and the World Agricultural Supply and Demand Estimates will include USDA’s first by-class wheat production estimates. Until then, you can stay updated with the latest crop conditions and harvest progress via the U.S. Wheat Associates weekly Harvest Report.
By USW Market Analyst Tyllor Ledford