By Claire Hutchins, USW Market Analyst
As marketing year (MY) 2018/19 draws to a close, customers of U.S. winter wheat are taking advantage of excellent buying opportunities on competitive pricing and high-quality, consistent supplies. Since the first week in January, the 2018/19 export sales pace for hard red winter (HRW) and soft red winter (SRW) surpassed last year’s pace for deliveries in the current marketing year (CMY) and the new marketing year (NMY).
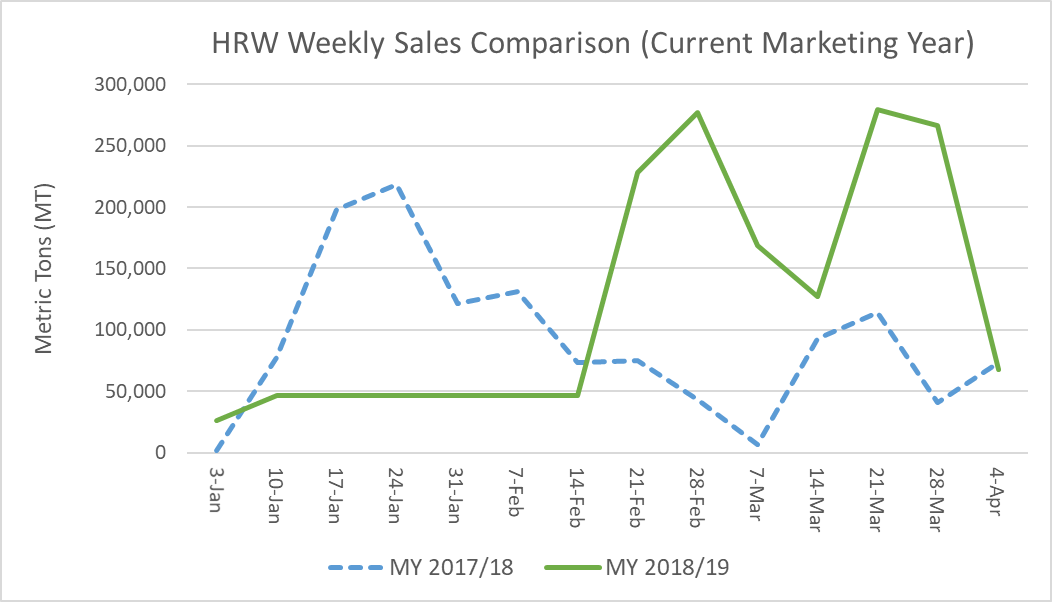
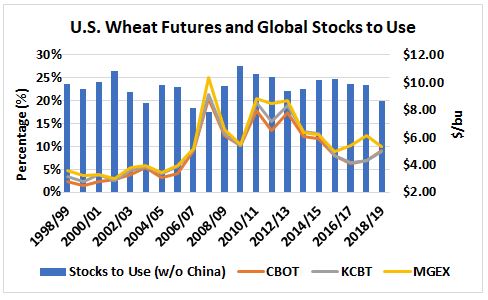
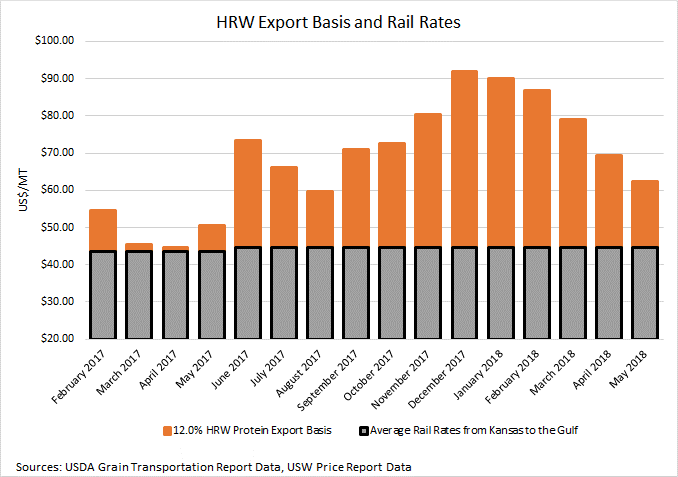
According to USDA commercial sales data as of April 4, 2019, HRW sales for 2018/19 delivery total 8.70 million metric tons (MMT). That is down 4% from this time last year but up 4% from the 5-year average of 8.33 MMT. Between February 14 and April 4, weekly sales of HRW for CMY delivery were significantly higher than the same six weeks in 2017/18 on low prices and high crop quality attributes. In the April 12 U.S. Wheat Associates (USW) Price Report, estimated FOB export price for 12% protein HRW (12% moisture basis) out of the Gulf at $222/MT for May 2019 delivery compared to $258/MT for delivery in May 2018. HRW export basis for the same delivery month, at $1.70/bu, is significantly lower than last year’s $1.95/bu. In addition to lower FOB export prices, the 2018/19 HRW crop features excellent milling and baking qualities.
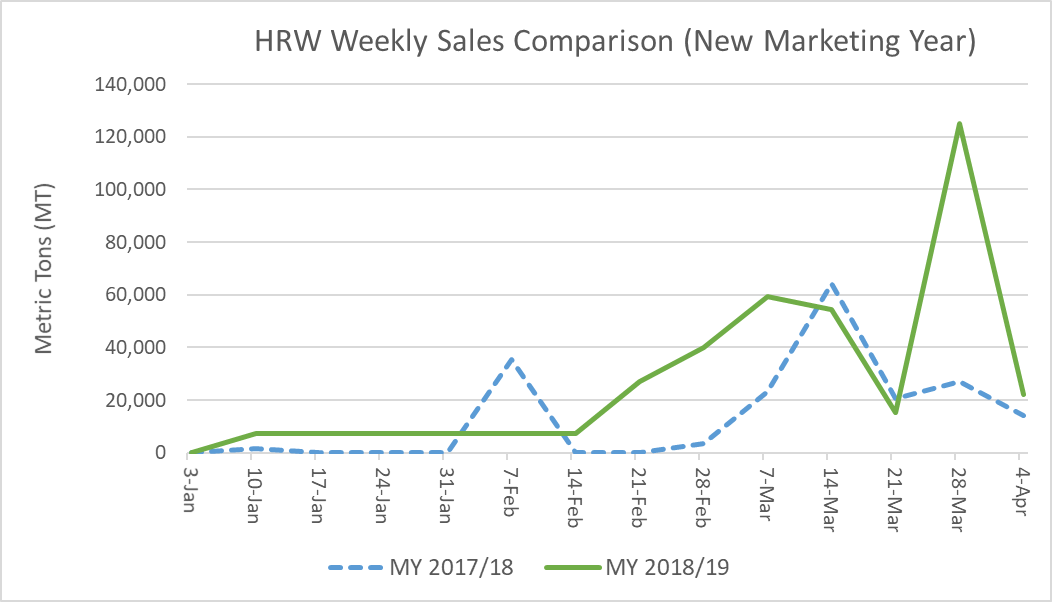
These market factors also support a significant uptick in HRW commercial sales into the NMY compared to NMY sales booked by the same time in 2017/18. HRW export sales for the 2019/20 marketing year total 396,000 metric tons (MT), up 64% from this time last year and 17% from the 5-year average. This represents the highest volume of HRW NMY sales to date since 2014/15. The most recent USW Price Report estimates 12% HRW FOB price for June 2019 delivery at $224/MT, compared to last year’s estimate of $259/MT for delivery in June 2018.
Members of the grain trade expect HRW FOB prices and export basis out of the Gulf to decrease steadily into the new marketing year on somewhat larger ending stocks, reduced inland logistical challenges, and favorable new crop conditions.
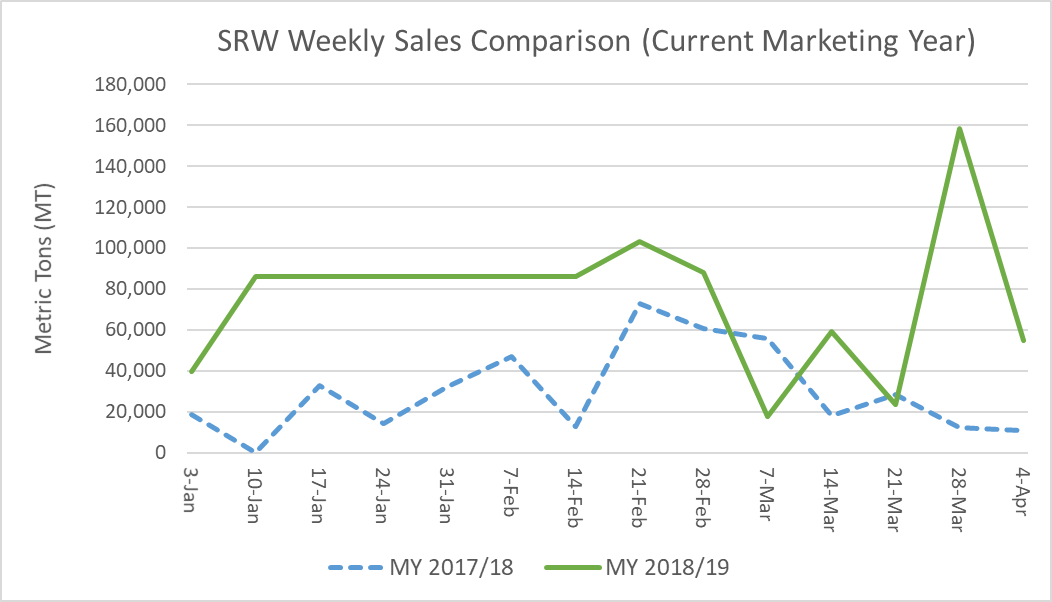
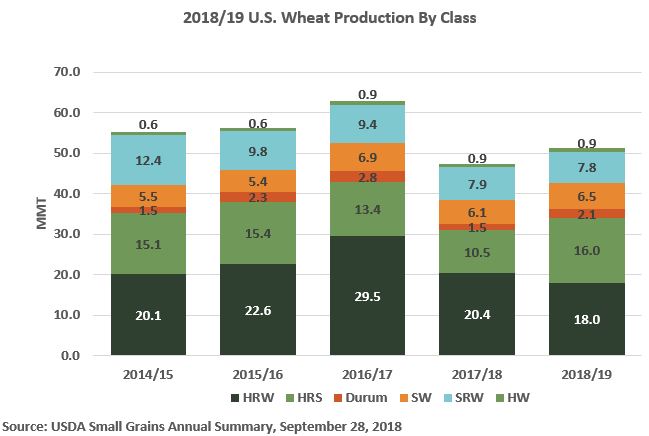
Turning to SRW, commercial sales to date for 2018/19 delivery total 3.30 MMT, up 36% year-over-year and 10% more than the 5-year average. This represents the highest volume of SRW commercial sales for CMY delivery since 2014/15. Competitive prices, higher than average protein levels and lower than average DON levels continue to elevate SRW export business through the second half of MY 2018/19. More information about the 2018/19 SRW crop is available at https://bit.ly/2ZdnMwi.
The latest USW Price Report valued the SRW export FOB price out of the Gulf at $204/MT for May 2019 delivery compared to $208/MT last year. SRW export basis for May 2019 delivery out of the Gulf at $0.90/bu is 5 cents less than last year’s estimate for May 2018 delivery.
Grain traders expect SRW FOB export prices and export basis to decline steadily into the first few months of MY 2019/20 despite tightening 2018/19 U.S. SRW ending stocks, which are forecast to fall to 4.57 MMT, 18% below 2017/18 and 7% below the 5-year average.
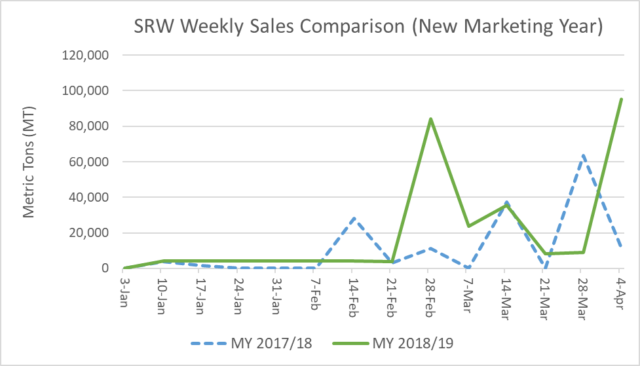
As with HRW sales, total SRW commercial sales for 2019/20 delivery are significantly higher than NMY sales booked this time last year. SRW commercial sales for NMY delivery total 302,000 MT, up 23% year-over-year and 15% from the 5-year average. This represents the highest volume SRW NMY sales to date since 2014/15 as customers look to lock in high quality supplies at globally competitive prices. The April 12 Price Report estimates SRW FOB price out of the Gulf for June 2019 delivery at $202/MT compared to last year’s estimate of $213/MT for the same delivery month in 2018.