Global durum production is expected to rebound in 2022/23, but stocks are likely to remain tight this season.
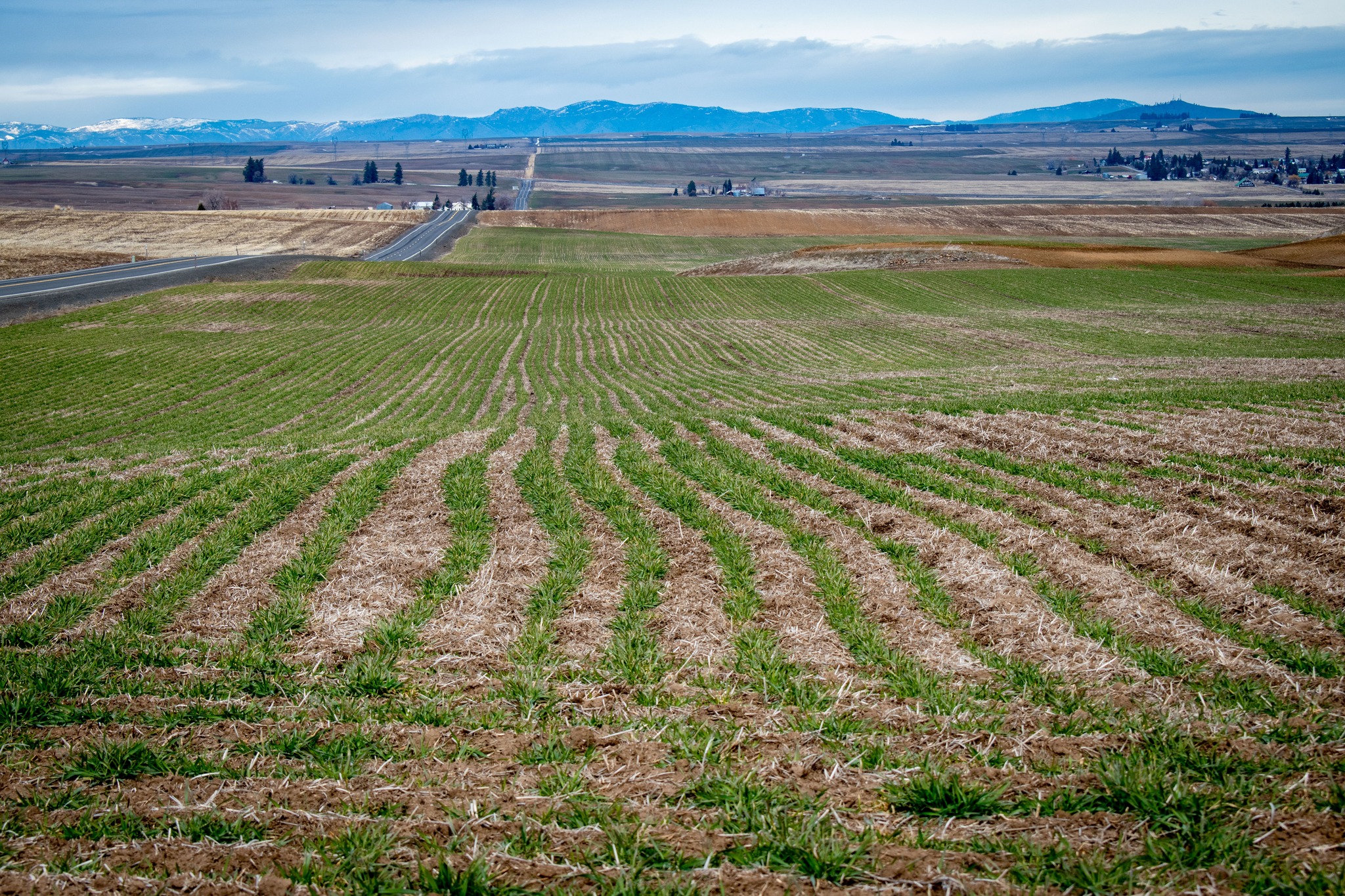
Total durum production in 2022/23 is expected to increase 10% to 33.9 MMT, led by increases in the United States, Canada, and Mexico. While durum production in North America looks good, production across Europe and North Africa is expected to fall. Reductions are led by the E.U. and Australia. Kazakhstan is expected to produce more durum but has banned wheat exports through September. Countries across North Africa, including Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia, grow significant domestic crops, but durum production this year is forecast to be smaller, increasing the need for imports.
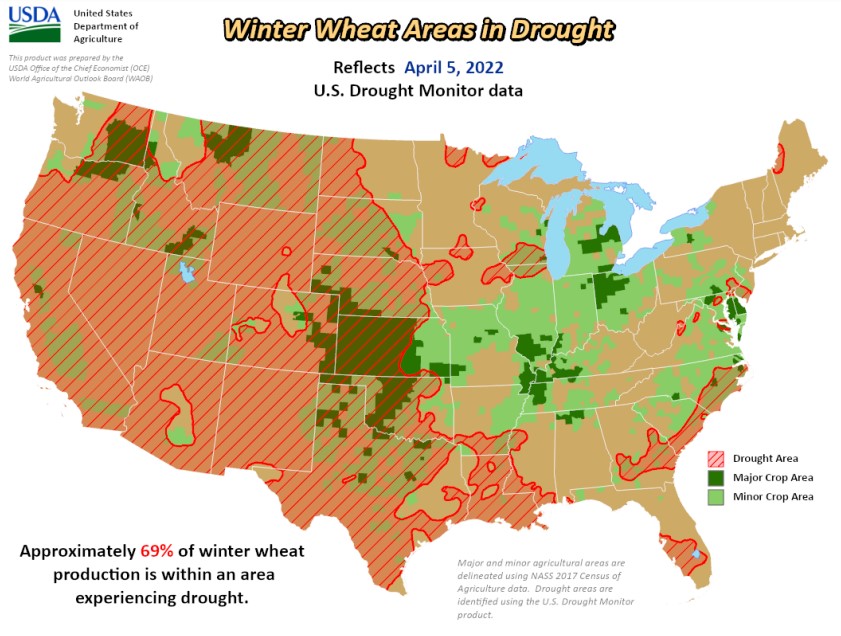
Drought Slashed Production
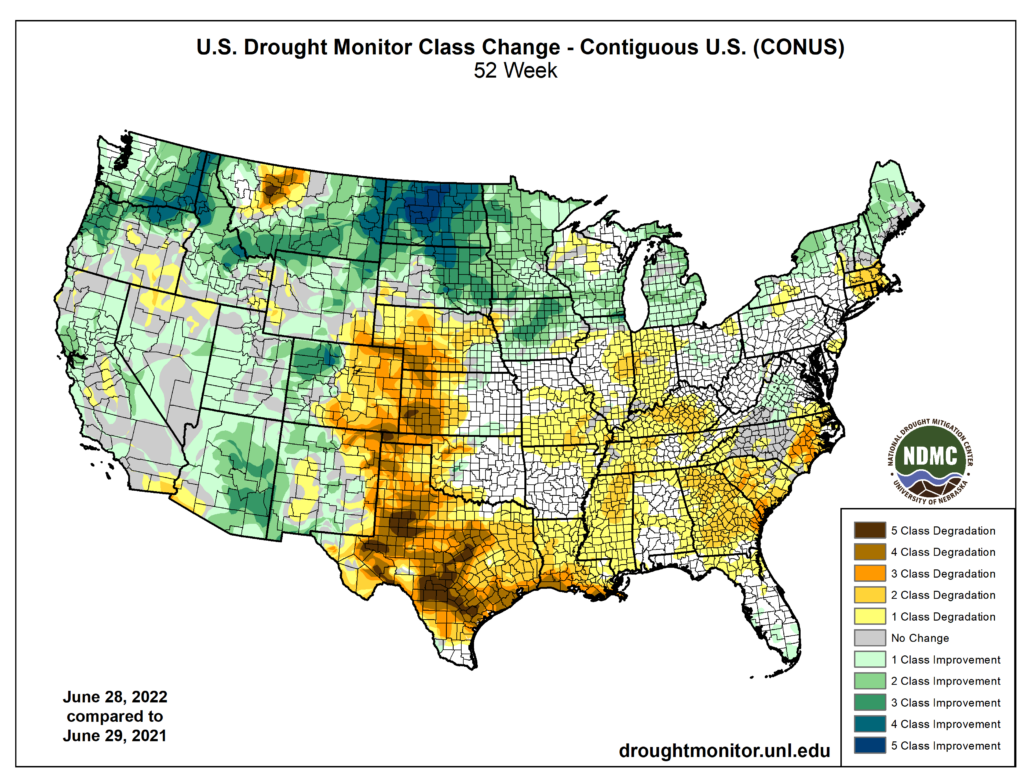
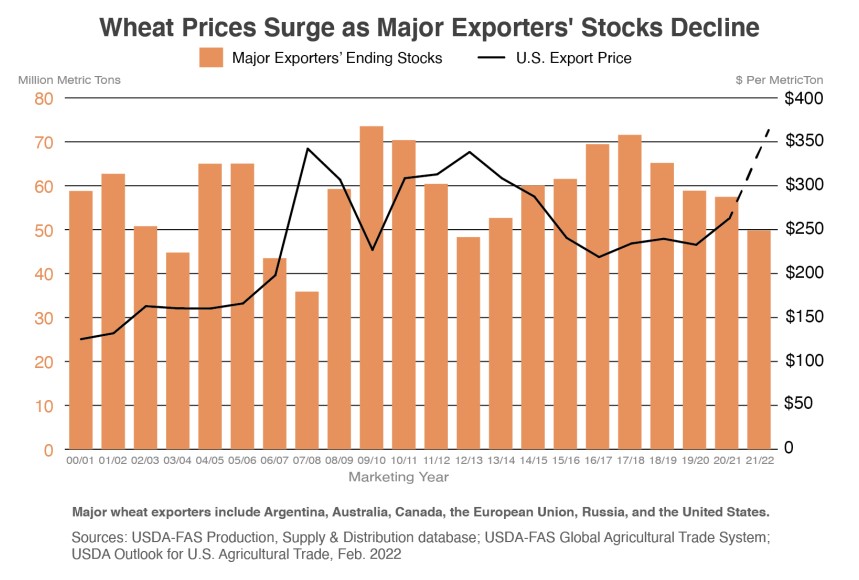
Last year, leading durum producers, including the United States and Canada, experienced hot weather and dry conditions that drastically cut production. Worldwide, beginning stocks of durum, according to Stratégie Grains, are 7.9 MMT, 1.6 MMT less than 2021/22. However, unlike last year, durum production estimates outside the E.U. and North Africa look good.
European Union
According to Stratégie Grains, a European research analyst, production across the European Union (E.U.) is seen falling to historically low levels due to dry weather. Stratégie Grains cut its E.U. durum production forecast by 600,000 MT between May and July. Stratégie Grains now forecasts production at 7.0 MMT, 9% behind 2021/22; if realized, this would be the lowest durum production since 1997.
Italy is by far the largest European durum user. Demand is pegged at 6.1 MMT. It produces a sizeable domestic crop but is experiencing a severe drought this year. An extremely dry winter and spring followed by hot weather since late spring has left the growing area parched, leading to the worst conditions in 70 years. The Italian government this month declared a state of emergency.
Heat is On in Europe
According to Coldiretti, an Italian agricultural lobby, the country’s durum and “common” wheat production this year is expected to fall 15% as the drought slashes yields. The Italian Millers’ Industrial Association expects durum production to fall 10% to 3.5 MMT.
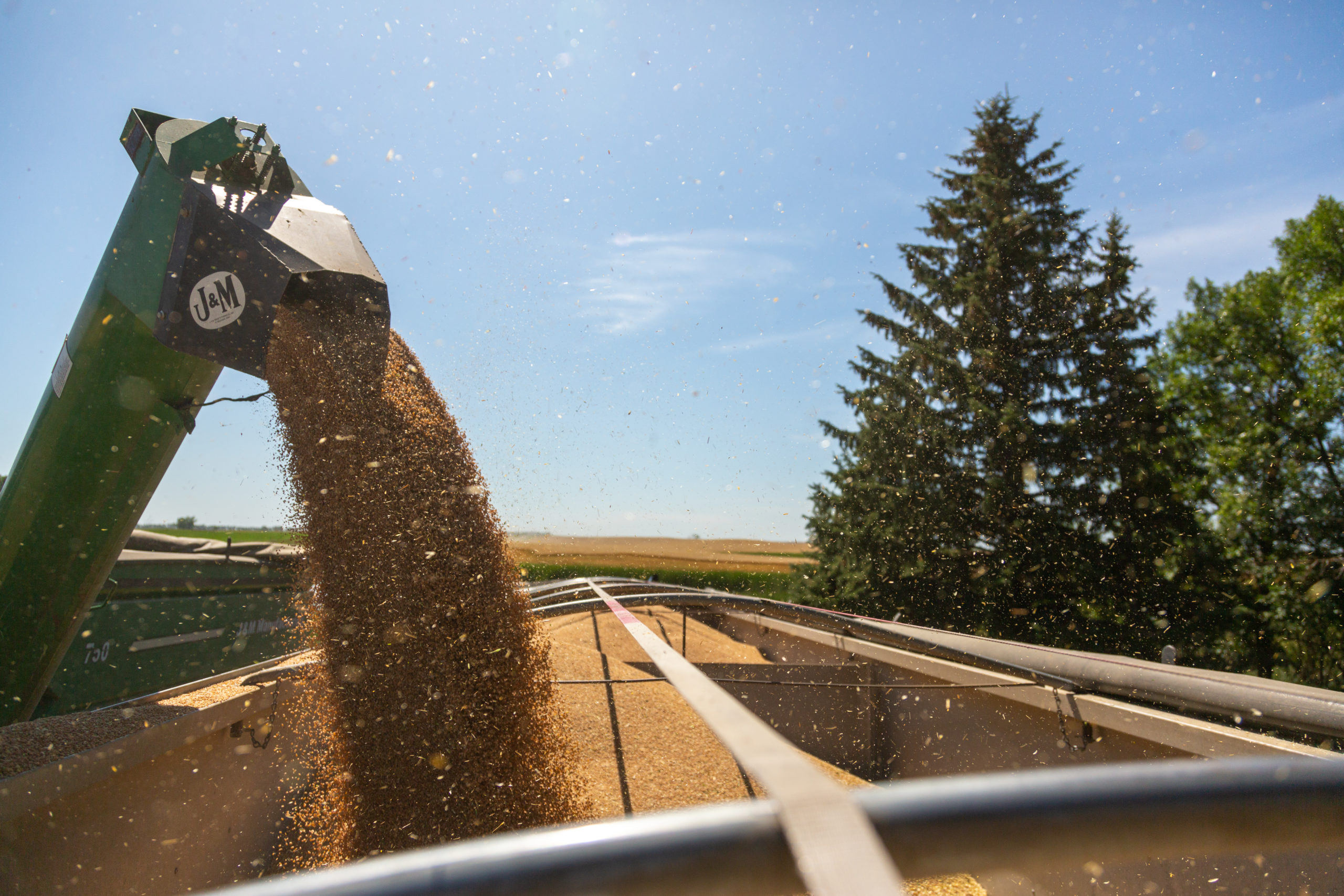
Italian durum production, estimated at 3.4 MMT, is expected to fall 2.6 MMT short of total demand. According to USDA sales data, for the 2022/23 marketing year, which began June 1, U.S. durum sales to Italy are up 124% compared to the same time last year.
United States
According to the USDA June Acreage Report, in the U.S., durum wheat planted area increased by 34% to 1.98 million acres (801,277 hectares). In the USDA’s July WASDE report, durum production in 2022/23 is forecast at 2.1 MMT, more than double 2021/22. Exports are expected to increase twofold to 800,000 MT.
The latest Crop Progress Report, published by USDA on July 18, rated 80% of North Dakota’s wheat good or excellent, while Montana reported 50% good or excellent. North Dakota and Montana together account for 93% of the durum wheat grown in the U.S.
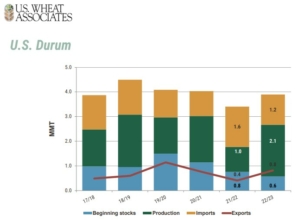
More Durum, More Sales. USDA’s first forecasts of U.S. durum production and exports in marketing year 2022/23 are up significantly. The market will be watching conditions closely from now until harvest.
Canada
Canada, usually the largest durum exporter globally, saw sluggish durum exports in the 2021/22 season. Western Canada experienced a devastating drought in 2021, which slashed yields and cut production by 53%. According to Statistic Canada, durum exports were 60% behind their 2020/21 pace through February, the latest data available.
This year looks different. Statistics Canada projects a 75% increase in supply. Canadian production is forecast at 5.52 MMT in 2022/23 due to increased seeded area and improved yields. Exports are also expected to increase 72% to 4.3 MMT.
Mexico
Durum production dominates Mexico’s total wheat production. USDA’s Foreign Agricultural Service in June 2022 dropped its forecast of Mexican wheat production slightly to 3.26 MMT for 2022/23. This change was based on information from industry and official government sources, reflecting unfavorable weather conditions and other factors. Mexico’s total durum and wheat exports are forecast at 850,000 MT.
Global Demand
Global demand for durum wheat is projected to increase 1.0 MMT to 32.9 MMT in 2022/23. As a result of the lower domestic production in many countries, global trade for durum is projected to increase 1.5 MMT to 7.4 MMT in 2022/23.
Stratégie Grains forecasts durum E.U. imports from non E.U. members to be 2.4 MMT, 1.0 MMT more than last year. Imports to Morocco are expected to increase 400,000 MT to 1.1 MMT.
Outlook More Optimistic
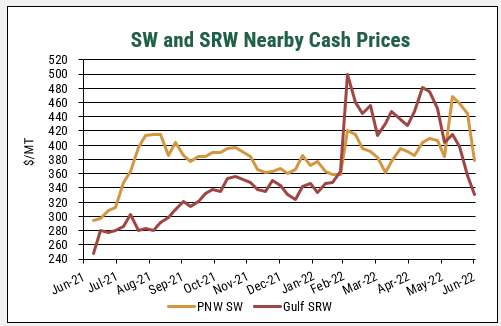
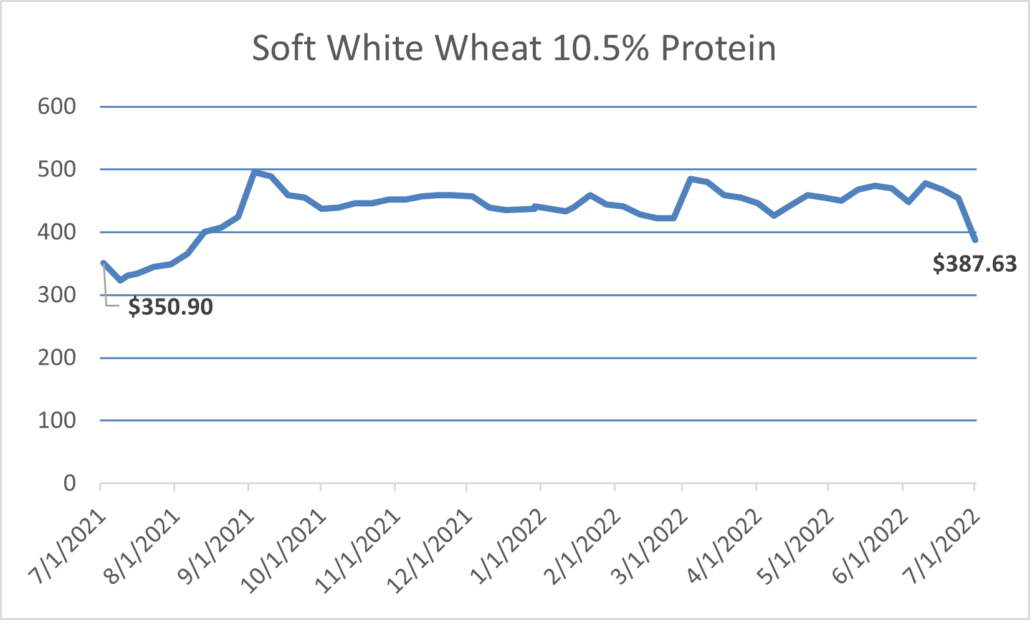
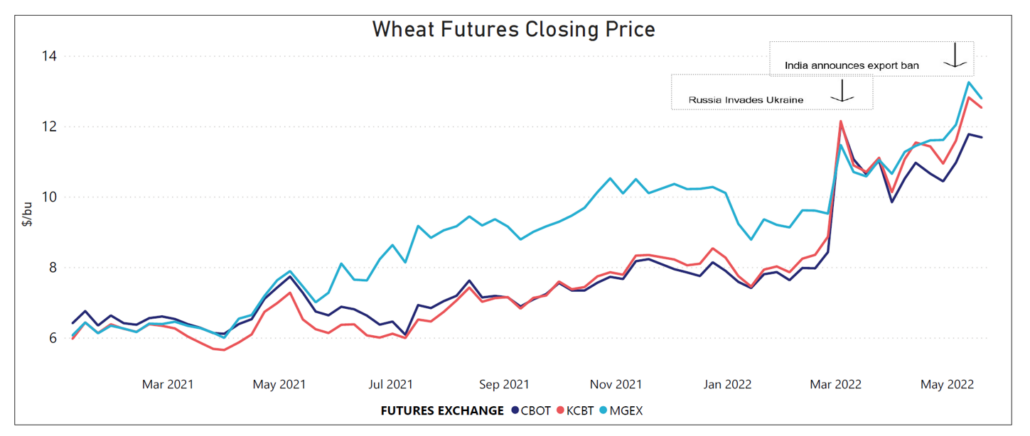
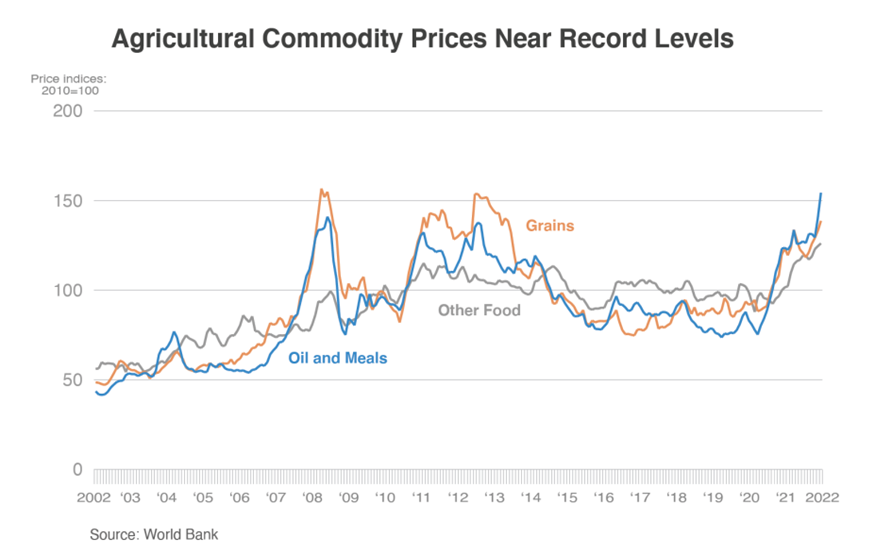
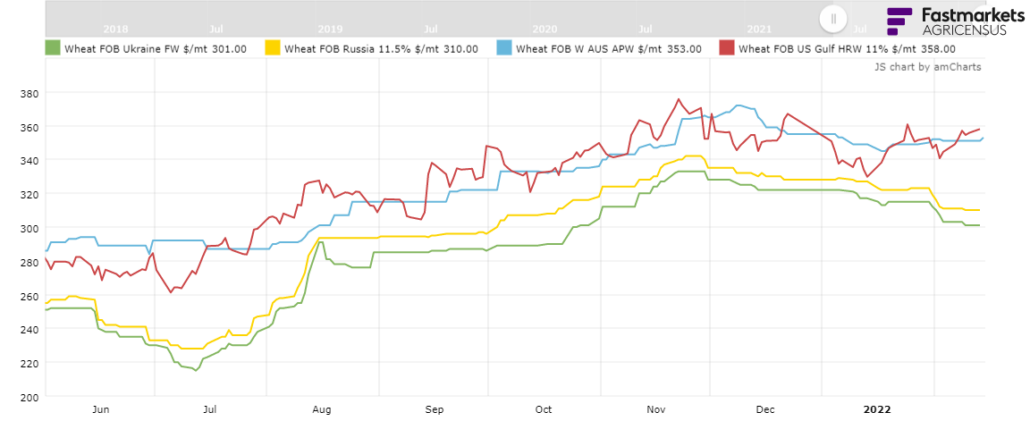
The tight ending stocks and a poor European harvest kept durum prices initially high at the start of 2022/23. Now increased planted acres and a positive outlook for the upcoming harvest have created an optimistic outlook for the North American durum crop and potentially easing export prices. However, another year of tight supplies and unknown variables, especially weather, between now and harvest could mean price fluctuations for the marketing year ahead.
The weekly Price Report, published by U.S. Wheat Associates, shows price indications, including durum wheat. USW also publishes annual crop quality data, including for durum wheat. The 2022/23 U.S. durum crop quality will be reported this fall.

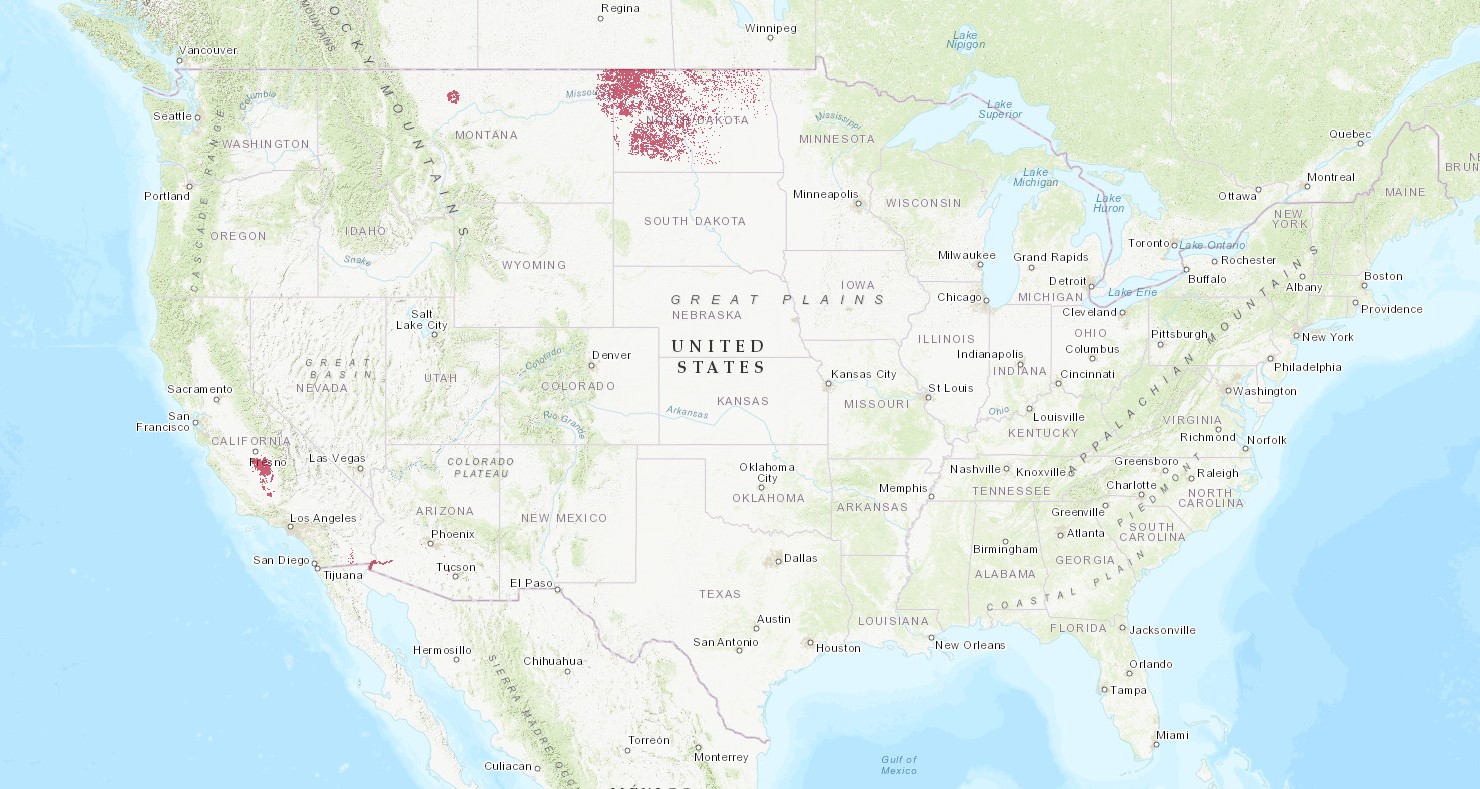
U.S. Durum Production is in North Dakota and Montana where Northern Durum is grown and shipped from Great Lakes and Pacific ports; Desert Durum® is grown primarily under contract in the desert Southwest and shipped via the Gulf or West Coast.
*Supply and demand estimates for durum wheat including world production, beginning stocks, EU-specific highlights, Italy, and Morocco, are based on Stratégie Grains’ July 15, 2022, Durum Report.
By USW Market Analyst Michael Anderson